Abstract
Background: Crisis management is a relatively new science in in Iran. researchers strategic managment consider to be more related to economics. Perhaps strategic management in military and defense sciences has a different nature. Research has been conducted on the relationship between crisis management and strategic, but a number of researchers still consider these two fields to be separate. This article examines the relationship between the basic and common components in these two areas. Materials and Methods: Pearson correlation, regression, one-sample t-test, and Friedman ranking tests have been performed using SPSS statistical analysis software at a significance level of 0.05. The statistical population of this study was 30 experts in these two fields who were selected purposefully. Results: Finally, after analyzing in the strategic management components, SWOT with a coefficient of 0.623, Mission-Vision with a coefficient of 0.553, Goals with a coefficient of 0.682, Execution with a coefficient of 0.660, Risk with a coefficient of 0.772, Planning with a coefficient of 0.678, Feedback with a coefficient of 0.502, Interaction with a coefficient of 0.538 and Mediating with a coefficient of 0.583, have a significant relationship with these components in crisis management. Conclusion: The conclusion of this study is that strategic management has a significant relationship with crisis management with a correlation coefficient of 0.819. And this means that these two areas are closely related and intertwined.
Keywords
Strategic Management, Crisis Management, Relationship Between Basic Components
1. Problem Statement
Nowadays, the subject of strategic management is widely used and this is a type of general plan. In the branches of management, efforts have been made to give great importance to this planning, this type of planning has been used in industry and organizations.
Strategic management is a management style and is not much different from other management models, but in terms of scope, comprehensiveness and methods, there may be some differences, and the implementation of this management method does not depend on the size or smallness of the organization and can be used everywhere.
Crisis management and strategic management were separate from each other in the past and there was no connection between them, and even researchers have considered these two categories to be completely unrelated to each other. Recently, researchers have tried to examine the common aspects of these two disciplines and identify a definite connection between them. In any case, identifying the exact nature of this connection is at the beginning of its journey, and with the generality that the strategic management process model has gained, many researchers and advocates of strategic management have not believed in this connection.
Strategic management allows organizations to function in a creative and innovative way, determine their destiny, and control the future. Crisis management conveys the implicit message that today the crisis is the main thing and no system is in a stable and long-term equilibrium. In addition, it is necessary to evaluate the professional of principals in crisis management
| [1] | Amani S, Tahmasbi S, Baneshi A, Poursadeghiyan M, Karimzadeh M. Factors Affecting Professional Competency of Iranian Preschool Administrators Based on Crisis Management Approach. Health in Emergencies & Disasters Quarterly. 2018; 3(4): 185-90 http://dx.doi.org/10.32598/hdq.3.4.185 |
[1]
.
Therefore, although organizations are not able to accurately predict and plan for the future, they must obtain the necessary information to overcome many known and unknown threats. This readiness will not be possible except by integrating strategic management and crisis management in organizations
| [2] | Hosseini, Seyed Yaqoub and Damnabi Asl, Anna. (2012). Investigating the impact of strategic management on the quality of crisis management operations. Crisis Management, 1(2), 77-86. |
[2]
.
For community resilience and disaster management planning, it is necessary to use appropriate information, models, and structures
| [3] | Çalışkan C, Üner S. Disaster literacy and public health: A systematic review and integration of definitions and models. Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness. 2021; 15(4): 518-27 https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2020.100 |
[3]
.
2. Research Objective
The overall objective of this research is to examine and analyze the relationship between the basic and effective components in the two disciplines of strategic management and crisis management. Because the process of these two disciplines is close to each other, and the integration of theory and practice of these two disciplines will lead to progress in both disciplines.
3. Definition of Idioms and Terms
3.1. Strategic Management
Strategic management is the art and science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating multidimensional decisions with an emphasis on integrating management, marketing, finance, production or services, implementation and development, information systems, etc. factors to achieve organizational goals
| [4] | Davari, Dordaneh; Shaneh Sazzadeh, Mohammad Hassan, Strategic Management from Theory to Action, Tehran, Athena Publishing, 2001. |
[4]
.
Decisions marked by confidence and quality often result from the process of strategic clarity within an organization
| [5] | Halbusi, Hussam Al. Ismail, Mohd Nazari. Omar, Safiah, Examining the Impact of Ethical Leadership on Employees’ Ethical Behavior: The Role of Organizational Justice and Employees’ Moral Identity, June 2019 Journal of Technology Management and Business 6(2) https://doi.org/10.30880/jtmb.2019.06.02.004 |
[5]
.
Strategic management is a process in which managers determine the long-term direction of the organization, formulate specific goals and functions, develop strategies that achieve these goals in light of internal and environmental conditions, and undertake the implementation of the determined programs
| [6] | ZARIBAF, MEHDI, & ALIZADEH HOSSEIN HAJLOU, TOHID. (2010). DEVELOPMENT OF STRATEGIC PLANNING IN IRAN FISHERIES INDUSTRY (CASE STUDY OF IRAN FISHERIES ORGANIZATION). JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT (PAJOUHESHGAR), 7(19), 18-33. SID. https://sid.ir/paper/151440/en |
[6]
.
Strategic management is the continuous process of creating, implementing and evaluating decisions that enable an organization to achieve its objectives. Strategic management allows an organization to be more proactive than reactive in shaping its own future; it allows an organization to initiate and influence -rather than just respond to- activities -and thus to exert control over its own destiny
.
Strategic decision-making in crisis situations has received much attention in professional and academic communities, however, the strategies adopted to deal with the crisis have received less attention
| [8] | Bargoni, A., Bertoldi, B., Giachino, C., & Santoro, G. (2022). “Competitive strategies in the agri-food industry in Italy during the COVID-19 pandemic: An application of K-means cluster analysis.” British Food Journal, 124(12), 4782-4799. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-072021-0738 |
[8]
.
Organizations need to adopt appropriate strategies to deal with the crisis
| [9] | Katare, B., Marshall, M. I., & Valdivia, C. B. (2021). “Bend or break? Small business survival and strategies during the COVID-19 shock. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 61, 102332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102332 |
[9]
.
3.2. Crisis Management
The process of planning, organizing, directing, and optimally controlling a crisis is called crisis management
| [10] | Hosseini, Maziar, Crisis Management, Shahr Publishing, First Edition, Tehran, 2008. |
[10]
.
A crisis refers to a sudden and unexpected event that threatens to disrupt an organization's operations.
| [11] | Alves, J. C., Lok, T. C., Luo, Y., & Hao, W. (2020). Crisis management for small business during the COVID-19 outbreak: Survival, resilience and renewal strategies of firms in Macau. [Preprint]. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-34541/v1 |
[11]
.
Crisis management is an applied science that, through systematic observation of crises and their analysis, seeks to find tools that can prevent the occurrence of crises or, in the event of a crisis, take action to reduce its effects, prepare for it, provide rapid relief, and improve the situation
.
Small and medium-sized companies should create a crisis plan in good times. Small companies survive and recover better from crisis events with proper crisis planning
| [13] | Muñoz, P., Kimmitt, J., Kibler, E., & Farny, S. (2019).“Living on the slopes: Entrepreneurial preparedness in a context under continuous threat. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 31(5-6), 413434. https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2018.1541591 |
[13]
.
Crisis management consists of a set of executive activities and managerial and political decisions related to different stages and all levels of the crisis in order to save, reduce losses and damage, prevent interruption of life, production, and services, maintain communications, preserve the environment, and finally repair and rebuild the damage
| [14] | Foster, H. D., and V. Wuorinen. 1976. British Columbia’s tsunami warning system: An evaluation. Syesis, 9: 115-122. |
[14]
.
It is recommended that we take significant s teps in elevating the confrontation and intervention level of crisis through the evaluation and improvement of safety cultural level
| [15] | Khammar A, Poursadeghiyan M, Marioryad H, Nabi Amjad R, Alimohammadi M, Khandan M. Patient Safety Climate and Its Affecting Factors Among Rehabilitation Health Care Staff of Hospitals and Rehabilitation Centers in Iran-Tehran. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2019; 17(1): 39-48 http://dx.doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.32598/irj.17.1.39 |
[15]
.
Although crisis management helps managers to solve critical problems, applying useful methods to prevent, control or deal with crises is not easily achieved, and in many organizations, departments are considered for this issue
| [16] | NikSeresht, Mohammad, Investigating the Relationship between Strategic Management and ICS Crisis Management System, First International Conference on Management, Business, Economics and Accounting, 2024. |
[16]
.
As crisis management is an ongoing process, continuous improvement by embedding lessons learned can minimize the risk of the next crisis
| [11] | Alves, J. C., Lok, T. C., Luo, Y., & Hao, W. (2020). Crisis management for small business during the COVID-19 outbreak: Survival, resilience and renewal strategies of firms in Macau. [Preprint]. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-34541/v1 |
[11]
.
3.3. Common Essential Components
3.3.1. SWOT
SWOT is an abbreviation of four words: Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat and is a framework used to evaluate the competitive position of the organization and develop strategic planning. SWOT Analysis. By conducting an external analysis, an organization identifies the critical threats and opportunities in its competitive environment
.
Vision and mission are among the documents of every organization that explain and specify its existential philosophy. Both of these are different for an organization, but they are often confused with each other.
3.3.2. Goals
The point that each organization must reach after examining and evaluating the theories of the internal and external environment, and the main and fundamental goal in each system is different from the performance of that system.
3.3.3. Execution
Strategy implementation is the implementation of a plan that specifies specific tasks and goals. Strategy execution is the implementation of a strategic plan in an effort to achieve organizational goals that include daily structures, systems, and operational goals that prepare the organization for success.
3.3.4. Risk
Risk is the uncertainty and awareness of the outcome of an action. Risk is the probability of a risk becoming actual. Risk is the probability of a risk becoming probable. Risk is equal to the severity multiplied by the probability.
3.3.5. Planning
A successful strategy has a comprehensive management plan, and planning is an integral part of a fundamental and fundamental management.
3.3.6. Feedback
A fundamental concept of control theory that refers to a loop. (Feedback), which returns the output of the system to the input and changes the input in some way, thus affecting the performance of the system.
3.3.7. Interaction
Effective communication between managers and employees and members of the organization requires good interaction between members of the organization and the entire environment and other organizations.
3.3.8. Mediating
The role of mediating variables such as (organizational culture, organizational structure, etc.) in the effect of strategic management on crisis management can be observed.
4. Research Background
Rahim Faghih Abdollahi and Sajjad Afsari, in an article titled The Role of Strategic Management in Organizational Crisis Management, have only addressed the role of strategic management in crisis management in general.
In an article titled "Identifying and Conceptualizing the Drivers of Strategic Strategy", Ali Bayazi Tehraband and colleagues defined a model to explain the drivers of strategic strategy by using the theory of multiple foundations.
Majid Pishvar and colleagues, in an article titled Examining the Relationship between Strategic Management Stages and Crisis Management (From the Perspective of Arak University of Medical Sciences Managers), have only examined the relationship between the stages of strategic management and crisis management.
Mohammad Hossein Nabizadeh Bahnamiri, in an article titled The Role of Strategic Management in Crisis Management, has examined the general role of strategic management in crisis management.
Mostafa Agha-Hosseini Ashkavandi and colleagues, in an article titled “Identifying and Prioritizing the Components of Strategic Foresight Capabilities, Crisis Management, and Human Resource Agility in Isfahan Blood Transfusion Organization Using Delphi and AHP Techniques,” have examined the components of foresight with a focus on human resources in Isfahan Blood Transfusion Organization.
Mohammad NikSeresht, in an article titled “Investigating the Relationship between Strategic Management and the Crisis Management ICS System,” has examined only the relationship between the performance of the crisis management ICS and strategic management.
A review of the research conducted on crisis management shows that most of these studies have emphasized specific aspects such as process pathology, urban planning and design methods, resilience and reconstruction, emergency evacuation spaces, and temporary housing. Among these studies, we can mention the research conducted at the Natural Disasters Research Institute, articles in the scientific journal of Crisis Management, and articles in the scientific journal of Knowledge of Prevention and Crisis Management
| [17] | Mollaei, Asghar. (Autumn, 2022), Explaining the foundations and strategies of a smart city with a sustainable approach in the field of crisis management (case study; Tehran metropolis). Quarterly Journal of Disaster Prevention and Management Knowledge, 11(3). 255-273. |
[17]
.
However, in the aforementioned research background, there are not many records of the basic components of crisis management and strategic management.
5. Research Questions
Is there a relationship between the basic components of strategic management and crisis management?
Is there a relationship between the two disciplines of crisis management and strategic management?
6. Research Hypotheses
Hypothesis H1: There is a correlation between the two variables under study.
Hypothesis H1: "Strategic management" has the ability to predict "crisis management".
Hypothesis H1: The regression coefficient of "strategic management" is not zero.
Hypothesis H1: The components of "strategic management" have the ability to predict "crisis management".
Hypothesis H1: The regression coefficient of the components of "strategic management" is not zero.
7. Research Method and Statistical Population
To analyze the basic components in crisis management and strategic management, common basic components were extracted by experts in these two fields, and a questionnaire was prepared by the researcher, and its validity was confirmed by experts, and its reliability was obtained using Cronbach's alpha after removing variables with zero variance of 0.960. The statistical population of this study was 30 experts in these two fields who were related to crisis management in education and teaching at higher doctoral levels and were selected purposefully (experts). In the inferential statistics section, Pearson correlation, regression, one-sample t and Friedman ranking tests were performed to analyze the observations and research data using SPSS statistical analysis software at a significance level of 0.05.
8. Data Analysis
Analyzing findings is of particular importance for any type of research to examine the validity and reliability of hypotheses. Today, in most research that relies on information collected from the subject under study; data analysis is considered one of the main and most important parts of research. Raw data are analyzed using statistical techniques and, after processing, are provided to users in the form of information. This section presents the results and findings obtained from the research, for which descriptive and inferential statistics methods have been used, so that the objectives and hypotheses of the research can be accessed by providing clear tables.
Initially, descriptive statistics methods were used to describe the data, including frequency statistics, mean, standard deviation, and skewness and elongation coefficients. In the inferential statistics section, Pearson correlation, regression, one-sample t-test, and Friedman ranking tests were used to analyze the observations and research information using SPSS statistical analysis software at a significance level of 0.05.
8.1. Descriptive Analysis
The following is the frequency and percentage of responses in each of the questionnaire questions. For example, in the first component of the strategic management variable, the percentage of responses was 0 percent "very low", 6.7 percent "low", 3.3 percent "medium", 30 percent "high" and 60 percent "very high".
8.2. Inferential Analysis
The role of descriptive statistics is actually to collect, summarize and describe quantitative information obtained from samples or communities. But the researcher usually does not end his work with describing the information, but tries to generalize what he has obtained from studying the sample group to larger similar groups. On the other hand, in most cases it is impossible to study all the members of a society.
Therefore, the researcher needs methods that can be used to generalize the results obtained from studying small groups to larger groups. The methods through which the characteristics of large groups are inferred based on the measurement of the same characteristics in small groups are called inferential statistics. In this section, the data are examined using correlation, regression, one-sample t-test and Friedman's ranking.
8.2.1. Investigating the Relationship Between Research Variables
Table 1. Results of the correlation study between research variables.
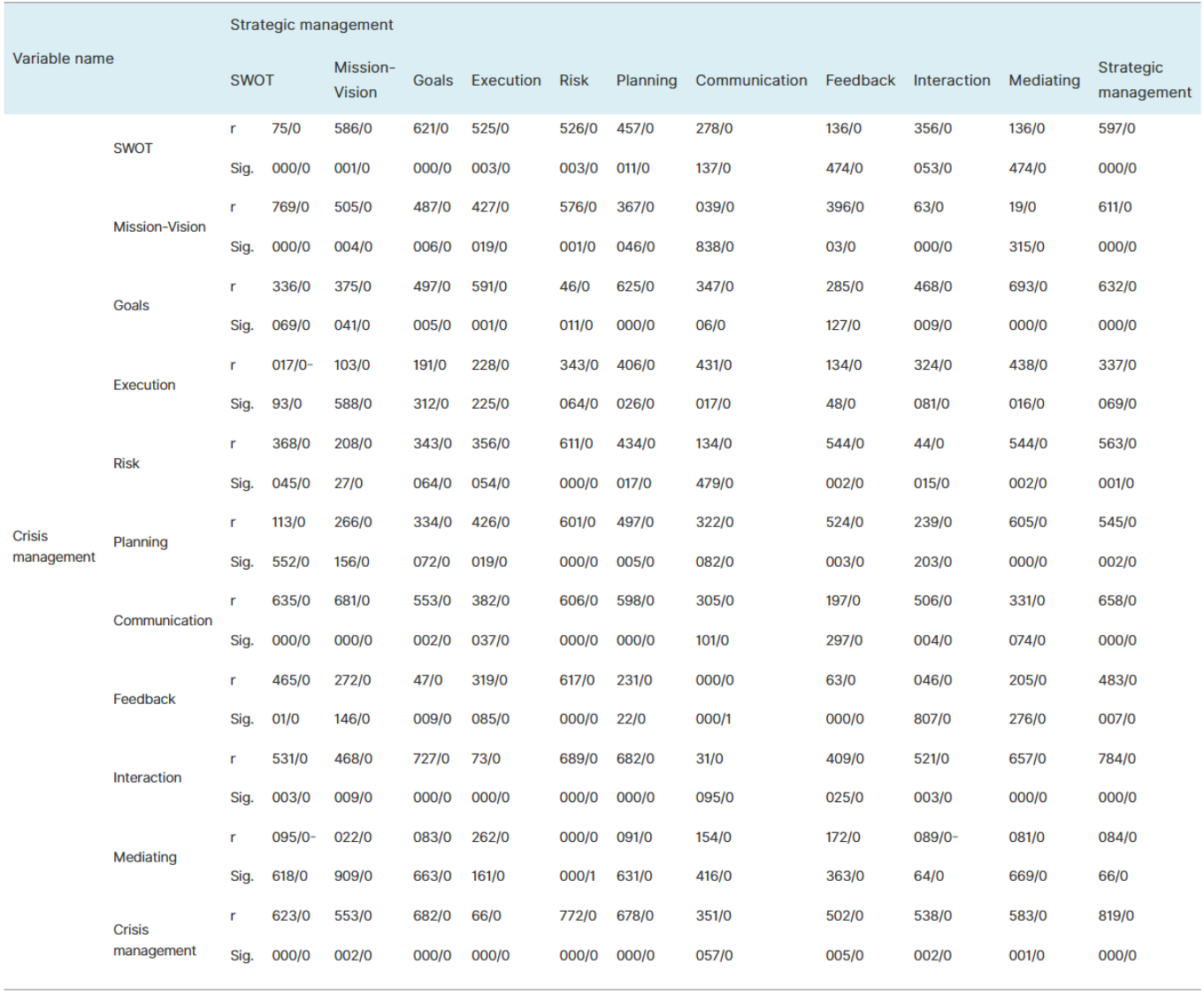
Most of the time, researchers want to know what kind of relationship there is between two or more variables. Correlation is the measure of the linear relationship between the variables. Note that two variables may have a relationship; but this relationship is not linear.
To find the correlation between two variables, we decide which method to use according to the type of variable under study. We use Pearson correlation when both of our variables are quantitative (continuous) and follow a normal distribution. If even one of the variables does not follow a normal distribution, we use Spearman's correlation coefficient. The value of the correlation coefficient varies between -1 and +1.
A value of zero indicates that there is no linear relationship between the variables. In the present study, Pearson correlation was used to investigate the relationship between the research variables, and the results are as follows. To test the correlation, statistical hypotheses are set as follows:
Hypothesis H0: There is no correlation between the two variables under study.
Hypothesis H1: There is a correlation between the two variables under study.
According to the correlation matrix, if the significant value for two indicators is less than 0.05, it means that the correlation coefficient between these two indicators is significant and the two indicators have a high correlation.
Strategic management with a correlation coefficient of 0.819 has a significant relationship with crisis management. Of the strategic management components, SWOT with a coefficient of 0.623, Mission-Vision with a coefficient of 0.553, Goals with a coefficient of 0.682, Execution with a coefficient of 0.660, Risk with a coefficient of 0.772, Planning with a coefficient of 0.678, Feedback with a coefficient of 0.502, Interaction with a coefficient of 0.538 and Mediating with a coefficient of 0.583 have a significant relationship with crisis management. Because the significant value corresponding to these coefficients is less than 0.05.
8.2.2. Regression and Forecasting
Forecasting "Crisis Management" by "Strategic Management"
Using regression, the predictive power of "Crisis Management" by "Strategic Management" was examined, the results of which are as follows.
Table 2. Summary of the regression model for predicting "Crisis Management" by "Strategic Management".
Multiple correlation coefficient | Coefficient of determination | Adjusted coefficient of determination | Estimation standard error | Durbin-Watson |
819/0 | 671/0 | 659/0 | 243/0 | 687/1 |
The results of
Table 2 show that based on the value of the coefficient of determination of the model (0.671), "strategic management" explained about 67 percent of the changes in the dependent variable "crisis management". The Durbin Watson statistic is 1.687 and is in the range of 1.5 to 2.5, so the lack of correlation between the residuals is accepted and there is no correlation between the residuals.
Table 3. Results of regression analysis of the prediction of "crisis management" by "strategic management".
Model | Sum of squares | Degrees of freedom | Mean squares | F | Significance value |
Regression | 373/3 | 1 | 373/3 | 012/57 | 000/0 |
Residual | 657/1 | 28 | 059/0 |
Total | 03/5 | 29 | |
To test the above regression, the statistical hypotheses are set as follows:
Hypothesis H0: "Strategic management" does not have the ability to predict "crisis management".
Hypothesis H1: "Strategic management" has the ability to predict "crisis management".
The results of the analysis of variance related to the regression model in
Table 3 show the significance of the combined and linear effects of the independent variable. Accordingly, the significance value of the relevant test, i.e. F, is equal to 0.000 and smaller than 0.05, and it can be concluded that the combined and linear effects of the independent variable on the "crisis management" variable are statistically significant.
Table 4. Impact coefficients and standard regression coefficients of predicting "crisis management" by "strategic management".
Model | Unstandardized impact coefficients | Standardized impact coefficients | t | Significance value |
B | Standard error | Beta |
Constant value | 643/1 | 395/0 | - | 165/4 | 000/0 |
Strategic management | 665/0 | 088/0 | 819/0 | 551/7 | 000/0 |
To test the significance of the regression coefficients, the statistical hypotheses are set as follows:
Hypothesis H0: The regression coefficient of "strategic management" is zero.
Hypothesis H1: The regression coefficient of "strategic management" is not zero.
Table 4 provides information on the regression effect coefficients, as well as the standard regression coefficients and information on the significance of these coefficients. The accuracy of the regression effect coefficient for "strategic management" (β = 0.819) and the significance value of the t-coefficient for this variable indicate a significant effect of this variable on "crisis management".
Prediction of "crisis management" by the components of "strategic management"
Using regression, the predictive power of "crisis management" by the components of "strategic management" was examined, the results of which are as follows.
Table 5. Summary of the regression model predicting "crisis management" by "strategic management" components.
Multiple correlation coefficient | Coefficient of determination | Adjusted coefficient of determination | Estimated standard error | Durbin-Watson |
855/0 | 730/0 | 589/0 | 267/0 | 857/1 |
The results of
Table 5 show that based on the value of the coefficient of determination of the model (0.730), the "strategic management" components explained about 73 percent of the changes in the dependent variable "crisis management". The Durbin-Watson statistic is 1.857 and is in the range of 1.5 to 2.5, so the lack of correlation between the residuals is accepted and there is no correlation between the residuals.
Table 6. Results of regression analysis of the prediction of "crisis management" by the components of "strategic management".
Model | Sum of squares | Degrees of freedom | Mean squares | F | Significance value |
Regression | 674/3 | 10 | 367/0 | 148/5 | 001/0 |
Residual | 356/1 | 19 | 071/0 |
Total | 5/03 | 29 | |
To test the above regression, the statistical hypotheses are set as follows:
Hypothesis H0: The components of "strategic management" do not have the ability to predict "crisis management".
Hypothesis H1: The components of "strategic management" have the ability to predict "crisis management".
The results of the analysis of variance related to the regression model in
Table 6 show the significance of the combined and linear effects of the independent variables. Accordingly, the significance value of the relevant test, i.e. F, is equal to 0.001 and smaller than 0.05, and it can be concluded that the combined and linear effects of the independent variables on the "crisis management" variable are statistically significant.
Table 7. Impact coefficients and standard regression coefficients of predicting "crisis management" by the components of "strategic management".
Model | Unstandardized impact coefficients | Standardized impact coefficients | t | Significance value | Multiple collinearity test |
B | Standard error | Beta | Tolerance statistic | VIF |
Value Fixed | 217/2 | 823/0 | - | 695/2 | 014/0 | - | - |
SWOT | 105/0 | 124/0 | 216/0 | 846/0 | 408/0 | 218/0 | 595/4 |
Mission-Vision | 065/0- | 122/0 | 107/0- | 532/0- | 601/0 | 353/0 | 831/2 |
Goals | 049/0 | 13/0 | 084/0 | 375/0 | 712/0 | 285/0 | 505/3 |
Execution | 072/0 | 233/0 | 087/0 | 308/0 | 761/0 | 176/0 | 683/5 |
Risk | 208/0 | 17/0 | 421/0 | 219/1 | 238/0 | 119/0 | 417/8 |
Planning | 183/0 | 098/0 | 32/0 | 858/1 | 079/0 | 48/0 | 084/2 |
Communication | 005/0 | 184/0 | 006/0 | 027/0 | 979/0 | 315/0 | 175/3 |
Feedback | 009/0- | 146/0 | 017/0- | 058/0- | 954/0 | 172/0 | May-81 |
Interaction | 016/0- | 143/0 | 019/0- | 11/0- | 913/0 | 484/0 | 067/2 |
Mediating | 013/0 | 096/0 | 026/0 | 138/0 | 892/0 | 4/0 | 499/2 |
To test the significance of the regression coefficients, the statistical hypotheses are set as follows:
Hypothesis H0: The regression coefficient of the "strategic management" components is zero.
Hypothesis H1: The regression coefficient of the "strategic management" components is not zero.
Table 7 provides information on the regression effect coefficients, as well as the regression standard coefficients, and information on the significance of these coefficients. The accuracy of the regression effect coefficient related to the "strategic management" components and the significance value of the t-coefficient related to these variables indicate the insignificant effect of these variables on "crisis management".
8.2.3. Friedman Ranking Test
Table 8. Results of the Friedman Ranking Test - Strategic Management.
Variable Name | Mean Ranks | Ranking |
Communication | 183/6 | 1 |
Interaction | 083/6 | 2 |
Execution | 5/8 | 3 |
Feedback | 667/5 | 4 |
SWOT | 583/5 | 5 |
Mission-Vision | 5/5 | 6 |
Planning | 383/5 | 7 |
Mediating | 367/5 | 8 |
Risk | 067/5 | 9 |
Goals | 367/4 | 10 |
In this study, the Friedman test was used to rank the indicators. The sample in question consists of 30 people. After performing the Friedman test, if its significance is proven (the significance value of the test is less than 0.05), the average ranks of the components can be compared with each other and the components with the highest and lowest ranks can be identified. In the Friedman test, the null hypothesis is based on the same average ranks among the groups. Rejection of this null hypothesis means that at least two groups have a significant difference among the groups.
Table 9. Results of the Friedman Ranking Test - Crisis Management.
Variable Name | Mean Rankings | Ranking |
Planning | 6 | 1 |
Feedback | 983/5 | 2 |
Risk | 917/5 | 3 |
Mission-Vision | 5/75 | 4 |
Mediating | 5/75 | 5 |
Execution | 483/5 | 6 |
Goals | 4/5 | 7 |
SWOT | 2/5 | 8 |
Communication | 883/4 | 9 |
Interaction | 633/4 | 10 |
9. Conclusion
According to the inferential statistics and regression and prediction tests and Friedman's ranking between the components of crisis management and strategic management and in relation to the experts' responses to the relationship between the components of these two fields, it shows that based on the value of the coefficient of determination of the model (0.671), "strategic management" has explained about 67 percent of the changes in the dependent variable "crisis management" and the results. of the analysis of variance related to the regression model show the significance of the combined and linear effects of the independent variable and also based on the value of the coefficient of determination of the model (0.730), the components of "strategic management" explained about 73 percent of the changes in the dependent variable "crisis management" and the accuracy in the regression effect coefficient related to the components of "strategic management" and the significance. value of the t-coefficient related to these variables indicates the insignificant effect of these variables on "crisis management" and in the Friedman ranking test in the ranking done for the components of "Strategic Management", the Friedman chi-square statistic is 17.237 and the corresponding significance value is less than 0.05 (0.045).
The Communication components with an average rank of 6.183, Interaction with an average rank of 6.083 and Execution with an average rank of 5.800 are ranked first to third, and in the ranking conducted for the "Crisis Management" components, the Friedman chi-square statistic is 14.265 and the corresponding significance value is greater than 0.05 (0.113).
The Planning components with an average rank of 6.000, Feedback with an average rank of 5.983 and Risk with an average rank of 5.917 are ranked first to third.
And in general conclusion, the relationship between the components of crisis management and strategic management shows that there is a close relationship between these two disciplines and that crisis management is intertwined with strategic management.
10. Suggestions
It is suggested that research be conducted on the effects of strategic performance on transformation and greater efficiency in crisis management.
It is suggested that research be conducted on strategic management knowledge in crisis managers and vice versa.
Abbreviations
SWOT | Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats |
AHP | Analytical Hierarchy Process |
ICS | Incident Command System |
Author Contributions
Mohammad Nikseresht: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Tahereh Adelkhani: Writing – original draft
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
References
| [1] |
Amani S, Tahmasbi S, Baneshi A, Poursadeghiyan M, Karimzadeh M. Factors Affecting Professional Competency of Iranian Preschool Administrators Based on Crisis Management Approach. Health in Emergencies & Disasters Quarterly. 2018; 3(4): 185-90
http://dx.doi.org/10.32598/hdq.3.4.185
|
| [2] |
Hosseini, Seyed Yaqoub and Damnabi Asl, Anna. (2012). Investigating the impact of strategic management on the quality of crisis management operations. Crisis Management, 1(2), 77-86.
|
| [3] |
Çalışkan C, Üner S. Disaster literacy and public health: A systematic review and integration of definitions and models. Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness. 2021; 15(4): 518-27
https://doi.org/10.1017/dmp.2020.100
|
| [4] |
Davari, Dordaneh; Shaneh Sazzadeh, Mohammad Hassan, Strategic Management from Theory to Action, Tehran, Athena Publishing, 2001.
|
| [5] |
Halbusi, Hussam Al. Ismail, Mohd Nazari. Omar, Safiah, Examining the Impact of Ethical Leadership on Employees’ Ethical Behavior: The Role of Organizational Justice and Employees’ Moral Identity, June 2019 Journal of Technology Management and Business 6(2)
https://doi.org/10.30880/jtmb.2019.06.02.004
|
| [6] |
ZARIBAF, MEHDI, & ALIZADEH HOSSEIN HAJLOU, TOHID. (2010). DEVELOPMENT OF STRATEGIC PLANNING IN IRAN FISHERIES INDUSTRY (CASE STUDY OF IRAN FISHERIES ORGANIZATION). JOURNAL OF INDUSTRIAL STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT (PAJOUHESHGAR), 7(19), 18-33. SID.
https://sid.ir/paper/151440/en
|
| [7] |
Gürel, Emet. Tat, Merba. SWOT Analysis: A Theoretical Review, January 2017 Journal of International Social Research 10(51): 994-1006
https://doi.org/10.17719/jisr.2017.1832
|
| [8] |
Bargoni, A., Bertoldi, B., Giachino, C., & Santoro, G. (2022). “Competitive strategies in the agri-food industry in Italy during the COVID-19 pandemic: An application of K-means cluster analysis.” British Food Journal, 124(12), 4782-4799.
https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-072021-0738
|
| [9] |
Katare, B., Marshall, M. I., & Valdivia, C. B. (2021). “Bend or break? Small business survival and strategies during the COVID-19 shock. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 61, 102332.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102332
|
| [10] |
Hosseini, Maziar, Crisis Management, Shahr Publishing, First Edition, Tehran, 2008.
|
| [11] |
Alves, J. C., Lok, T. C., Luo, Y., & Hao, W. (2020). Crisis management for small business during the COVID-19 outbreak: Survival, resilience and renewal strategies of firms in Macau. [Preprint].
https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-34541/v1
|
| [12] |
Nateghi Elahi, Fariborz, Earthquake scenario for the mega-city of Tehran, May 2001, Disaster Prevention and Management An International Journal 10(2): 95-101
https://doi.org/10.1108/09653560110388618
|
| [13] |
Muñoz, P., Kimmitt, J., Kibler, E., & Farny, S. (2019).“Living on the slopes: Entrepreneurial preparedness in a context under continuous threat. Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 31(5-6), 413434.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08985626.2018.1541591
|
| [14] |
Foster, H. D., and V. Wuorinen. 1976. British Columbia’s tsunami warning system: An evaluation. Syesis, 9: 115-122.
|
| [15] |
Khammar A, Poursadeghiyan M, Marioryad H, Nabi Amjad R, Alimohammadi M, Khandan M. Patient Safety Climate and Its Affecting Factors Among Rehabilitation Health Care Staff of Hospitals and Rehabilitation Centers in Iran-Tehran. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal. 2019; 17(1): 39-48
http://dx.doi.org/dx.doi.org/10.32598/irj.17.1.39
|
| [16] |
NikSeresht, Mohammad, Investigating the Relationship between Strategic Management and ICS Crisis Management System, First International Conference on Management, Business, Economics and Accounting, 2024.
|
| [17] |
Mollaei, Asghar. (Autumn, 2022), Explaining the foundations and strategies of a smart city with a sustainable approach in the field of crisis management (case study; Tehran metropolis). Quarterly Journal of Disaster Prevention and Management Knowledge, 11(3). 255-273.
|
Cite This Article
-
APA Style
Nikseresht, M., Adelkhani, T. (2025). Linking Crisis Management and Strategic Management (Analysis of the Relationship of Common Essential Components). American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 10(3), 40-49. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
ACS Style
Nikseresht, M.; Adelkhani, T. Linking Crisis Management and Strategic Management (Analysis of the Relationship of Common Essential Components). Am. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 2025, 10(3), 40-49. doi: 10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
AMA Style
Nikseresht M, Adelkhani T. Linking Crisis Management and Strategic Management (Analysis of the Relationship of Common Essential Components). Am J Eng Technol Manag. 2025;10(3):40-49. doi: 10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
-
@article{10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12,
author = {Mohammad Nikseresht and Tahereh Adelkhani},
title = {Linking Crisis Management and Strategic Management (Analysis of the Relationship of Common Essential Components)
},
journal = {American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management},
volume = {10},
number = {3},
pages = {40-49},
doi = {10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ajetm.20251003.12},
abstract = {Background: Crisis management is a relatively new science in in Iran. researchers strategic managment consider to be more related to economics. Perhaps strategic management in military and defense sciences has a different nature. Research has been conducted on the relationship between crisis management and strategic, but a number of researchers still consider these two fields to be separate. This article examines the relationship between the basic and common components in these two areas. Materials and Methods: Pearson correlation, regression, one-sample t-test, and Friedman ranking tests have been performed using SPSS statistical analysis software at a significance level of 0.05. The statistical population of this study was 30 experts in these two fields who were selected purposefully. Results: Finally, after analyzing in the strategic management components, SWOT with a coefficient of 0.623, Mission-Vision with a coefficient of 0.553, Goals with a coefficient of 0.682, Execution with a coefficient of 0.660, Risk with a coefficient of 0.772, Planning with a coefficient of 0.678, Feedback with a coefficient of 0.502, Interaction with a coefficient of 0.538 and Mediating with a coefficient of 0.583, have a significant relationship with these components in crisis management. Conclusion: The conclusion of this study is that strategic management has a significant relationship with crisis management with a correlation coefficient of 0.819. And this means that these two areas are closely related and intertwined.
},
year = {2025}
}
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
-
TY - JOUR
T1 - Linking Crisis Management and Strategic Management (Analysis of the Relationship of Common Essential Components)
AU - Mohammad Nikseresht
AU - Tahereh Adelkhani
Y1 - 2025/09/19
PY - 2025
N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12
DO - 10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12
T2 - American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management
JF - American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management
JO - American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management
SP - 40
EP - 49
PB - Science Publishing Group
SN - 2575-1441
UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20251003.12
AB - Background: Crisis management is a relatively new science in in Iran. researchers strategic managment consider to be more related to economics. Perhaps strategic management in military and defense sciences has a different nature. Research has been conducted on the relationship between crisis management and strategic, but a number of researchers still consider these two fields to be separate. This article examines the relationship between the basic and common components in these two areas. Materials and Methods: Pearson correlation, regression, one-sample t-test, and Friedman ranking tests have been performed using SPSS statistical analysis software at a significance level of 0.05. The statistical population of this study was 30 experts in these two fields who were selected purposefully. Results: Finally, after analyzing in the strategic management components, SWOT with a coefficient of 0.623, Mission-Vision with a coefficient of 0.553, Goals with a coefficient of 0.682, Execution with a coefficient of 0.660, Risk with a coefficient of 0.772, Planning with a coefficient of 0.678, Feedback with a coefficient of 0.502, Interaction with a coefficient of 0.538 and Mediating with a coefficient of 0.583, have a significant relationship with these components in crisis management. Conclusion: The conclusion of this study is that strategic management has a significant relationship with crisis management with a correlation coefficient of 0.819. And this means that these two areas are closely related and intertwined.
VL - 10
IS - 3
ER -
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
