Abstract
From the 1900s to 2020s, humans believed photons were massless particles. However, solar wind is made of ionized particles such as hydrogen and helium stripped of electrons. This study is one of the first to identify photons as electrons based on analysis with photosynthesis, oxidation reduction reactions, ionization energy, vertical electric fields, and negative air ions (NAIs), when O2 combines with electron to form O2-. Earth's electrical field is around 100-300 V/metre which further suggests charge is due to light photons or electrons. Electron kinetic and ionization energies of both electrons (e-) and photons are analyzed. A photon electron radiation flux analysis across each planetary body also quantifies photons/m2, which helps to advance systems and models in orbit and at surface of planets. After first discovery of photons as electrons from Kole Lutz in 2024, research helps to quantify electron interactions, absorption/emission to improve weather climate models, photosynthesis, power systems (PV Cells, detectors, etc.), corrosion redox reactions, and materials across a variety of fields from energy, communication to biology and space systems. Research holds potential to increase instrument sensitivity for Earth and planetary science, physics, lasers, communication, and to characterize absorption spectra, and light flux from stars.
Keywords
Physics, Astrophysics, Space Science, Oxidation, Photonics, Quantum Mechanics
1. Introduction
This study aims to collect and analyze literature identifying photons as electrons based on data from negative air ions, ionization energy analysis, photosynthesis and redox reactions, and planetary solar radiation data and vertical electric fields.
From 1900s to 2020s, humans believed photons were massless particles. The concept and discussion progressed in 1905 when Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect and relativity and was popularized by Gilbert Lewis who coined “photon”. If a photon has no mass, how would Kinetic Energy (KE), E=pc or, or E=mc
2 exist? As light is correlated to solar wind density
) in particles/cm
3, solar wind is made of plasma with ionized hydrogen, electrons (e-), e- fragments & protons with 8.5 ± 1.3%He
.
Stellar Composition, Corona, Nuclear Fusion
The sun is a yellow dwarf (G-type V) star of hot gasses, hydrogen (92.1%) and He (7.9%) with mostly free-floating electrons and protons. As e- are stripped from gasses at surface, ionized He such as He
2+ is abundant after H
+.
| [2] | Zuccaro, D. E., "Analysis of the Simulation of the Solar Wind," ASTM/IES/AIAA Space Simulation Conference, 14-16 Sept 1970. |
[2]
Figure 1. a & b) Electron Absorption and Emission, c) Vertical Electric Field.
Two electrons or positrons are generated from two H-H atoms combining at core and surface from fusion, where (ν) neutrinos and neutrons can also be emitted. Helium-3 fusing with helium-3 nuclei produces 86% of our helium-4
| [3] | Siegel, E. (2022, October 12). The Sun’s energy doesn’t come from fusing hydrogen into helium (mostly). Forbes. |
[3]
. To build up to helium-4, proton-proton chain, electrons (e-) in helium and hydrogen move to higher energy orbits, where e- reshuffling releases energy. Energy released is e- and positrons (β +) &
released with ~3.5 MeV for He. When an electron (e-) changes levels after absorption or emission, an atom emits electromagnetic radiation of photon-like particles with exact energy that is lost by the e- moving to a lower energy level. Electron (e-) energy displacement would be correlated with ejected particles such as partial or whole quasi-electrons with ejected energy or quanta is energy lost by the e- moving to lower energy level.
where
is scattering angle from
f-
i with bohr radius and also solar radius 696,265km. Solar photosphere at the surface is 100-400 km, where e- accumulate, is measured at .21 g/m
2 density. Surface electrons reach limit distance at a velocity of 1.3 × 10
-6 m/s. Data suggests sun has vertical magnetic (B) field gradient of 3 G km
−1 and horizontal B-field gradient of 0.3 G km
−1.
At the star’s surface, electromagnetic radiation is emitted in the form of particles associated with scattering and emission spectra of electrons, where absorption and emission spectra would be correlated with ejected Quasi-Electrons
| [5] | Lutz, 2024. Absorption and Emission Spectra Correlated with Ejected Quasi-Electrons, March 2024, ResearchGate |
[5]
.
The lightest common gasses (He and H) are typically most abundant in Earth’s upper atmosphere, with 62-84% He and 36-10% H 1000-650 km, respectively. Also, Van Allen Radiation belt (inner 1,000-12,000km) and outer belt 13,000 - 60,000km) are a sink for particles such as electrons. Energy flux of 1361 (W/m²) is received at top of Earth's atmosphere and 1000 W/m² at sea level, atmosphere absorbs 23% and the surface absorbs 48%. Sunlight is 42-44% visible light, 3% UV, and 53% IR. ~49% of solar radiation is IR is between 700nm-1mm. Sunlight at surface is 52-55% IR (> 700 nm), 42% visible (400-700 nm).
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Ionisation Energy
Kinetic Energy (KE) would be correlated with ejected particles & electrons. Eq
7 assumes a linear sphere particle where E
n is ionisation energy and r is radius. Further models may be based on energy transition and Bohr radius.
=+FIR+Foptical+...Fn(8)
where F is Total Force from electromagnetic spectrum range measured in energy units (joules, calories) or watt/m2. Ionisation Energy (En) is the lowest energy range to remove the loosely bound electron typically in valence cloud. En increases with high charge states and electron spin pairs. As electrons are stripped from gasses on solar surface, Ionisation Energy (En) of H is (-13.59eV) and He (-24.6 eV), which would correlates to observed fluxes from ejected e-. KE analysis is outlined in section 3 Results.
2.2. Negative Air Ions (NAIs) from Electrons
NAIs can be generated by a certain wavelength of light when air molecules O
2/N
2 are ionised, or gain e-. NAIs are composed of e- and negatively charged molecules such as O
2−, H
2O, CO
3−, OH
-, NO
3−, and others. NAIs are formed and generated primarily by sunlight, radiant or cosmic rays, as well as plant-based sources of energy, lightning and lenard effect.
| [6] | Jiang, S. Y., et al (2018). Negative Air Ions and Their Effects on Human Health and Air Quality Improvement. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(10), 2966. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102966 |
[6]
) NAIs such as O
2- form when e- from light or H
2O react to join e- cloud of O
2 via exothermic reaction:
With 8e- per O, shared valence e- forms 1 sigma bond and 1 pi bond, with 120 pm (.123nm) bond length, where O2- suggests O2 has extra space and smaller fragments of e-.
With NAI generation in
Figure 2, this may suggest 2X more electrons scattering from light photons. UV-mediated ionization is dominant NAI source above 60 km of atmosphere, where NAIs accept radiated electrons
. If electrons have greater mass higher up in atmosphere, this may suggest higher O
2 and N
2 charge states. With materials exposed to atomic oxygen (AO) at altitude of 160–560 km, higher UV rays and higher mass elements split O
2. AO degrades and corrodes polymers from high fluxes which are observed in optic spectrum with reactions and degradation of the 11 types of thermal control materials on ISS
. With electrons transferred from sunlight and with 157 peer reviewed articles from (Jiang, et al, 2018) on NAI, this suggest photons are electrons or quasi particles.
2.3. Earth & Planetary Vertical Electric Fields
Systems and organisms evolved within Earth's magnetic (B) field .2 to .7 Gauss (20-80µT) and electric (E) field for billions of years
.
Figure 3. Earth’s Vertical Electric Fields.
Figures above outline E field magnetic & B-field flux that acts on flux gradient and ions. Electrical field (Ez) is around 100-300 V/metre with closer to 100V/m or or Nm/C at surface, suggesting Electric field (Ez) increases with altitude km, due to air medium density, and decreases with lower electron mass near surface. As the electric conductivity (σ) of air gradually grows from ~10 to ~10 Siemen /metre, there is a weak conduction current of atmospheric ions moving in the atmospheric electric field, about 2 picoamperes per m2. This also correlates with thunderstorm activity or Carnegie curve.
Although the mass of e- photons are not currently known and may range considerably, photon flux radiation data can be compared with e- current density data in watts/m
2 per Volt. With 1,360 watts /m
2 at Earth’s atmosphere, 168-1000 W/m
2 at Earth’s surface and 1kW per m
2 at equator, electron scattering or mass loss over 400km would suggest 3.4Volts/km or .034V/metre is released on average, which may further be correlated with EQS model outlined below. However, there is around 1E12 O
2 and N
2 around 100 km vs 1E8 particles/cm
3 at 400 km based on density of atmospheric species as a function of altitude
. Future work may factor in atmospheric pressure on electron quanta scattering and B-field measurements.
Moreover, magnetic (B) field and Electric (E) fields permeate across skin with cellular effects. With ~150V less Newtons/Coulomb per min after E-field separation in some indoor environments, this is 216 kV less per day on cells and organisms. Effects are further discussed in next section on reduction and oxidation reactions such as photosynthesis.
2.4. Photosynthesis and Redox
Oxidation and reduction reactions involve loss or gain of electrons. In photosynthesis, H2O is oxidized with loss of e-, while CO2 is reduced, or gains electrons to form glucose in chlorophyll plant cells. When fruit are exposed to oxygen or sunlight electrons, oxidation occurs and turns food brown. Electromagnetic light gradient provides catalyst for the below photosynthesis reaction in chlorophyll to split H2O, capture CO2 and generate O.
Figure 4. Photosynthesis where e- are removed from H2O and absorbed in PSI, PSII and proteins in Electron Transport Chain (ETC).
Figure above suggests photons impart electrons on ETC chains. Figure outlines e- transport where e- transfers to P680, and PSI before e- transfer to NADPH to synthesize ATP from ADP. With H2O, PO4 and light energy or e- to convert ADP to ATP, e- light flux acts on bonded or valence e- within phosphate groups to unfold/refold PO4 groups. This suggests bidirectional KE flux of e- from ∇f (e-light) and ∇f (e-Membrane) is a function of ATP synthesis rates and production, voltage gated ion channels, & output of membrane proteins.
Figure 5. Cell Membrane Potential where Photons or Electrons follow vector Electric (E) Field Gradient.
2.5. Redox & Corrosion in Solids and Metals
Most literature suggests rust forms from oxides and hydroxides of iron, exposed to oxygen and H
2O. As UV and IR light accelerate corrosion in metals
corrosion potential increases under sunlight. Loss of valence e- in atoms creates scattering and ejection of surface atoms, which can lead to corrosion over time. Redox e- exchange would be increased at surface defects and holes. Incoming photons and NAIs act on valence e- and atoms at surface, this suggests photons or electrons are a primary force for rust in metals and solids.
3. Results
3.1. Kinetic Energy Analysis
As some Kinetic Energies (KE) are based on 1/2mv2 (eV), particle fluxes are modeled based on KE = mv in (ev). KE (eV) = hc/lambda suggests a 1nm electron has 1.5eV energy, which is 2.57% below KE or 0.04eV less than IR at 800 nm that was associated with photon flux.
As higher KE flux is correlated with wavelength, Light from the sun is 52 to 55% IR (> 700 nm), 42% visible (400 to 700 nm), which suggests 1.77eV (700 nm) to 3.099eV (400 nm). UVB (280–315 nm), and UVC (100–280 nm).
Figure 6. Photon Energy (eV) Infrared (300-700nm) in Similar Range as 1.5eV Electron.
Table 1. Starlight e- Wavelength Kinetic Energy Analysis.
Starlight Electron Wavelength Kinetic Energy Analysis |
| nm | meters | KE (eV)= hv/lambda |
IR-l | 800.00 | 8.00E-07 | 0.00242 |
IR-h | 400.00 | 4.00E-07 | 0.00484 |
uvb-l | 700.00 | 7.00E-07 | 0.00276 |
uvb-h | 315.00 | 3.15E-07 | 0.00614 |
uvc-l | 280.00 | 2.80E-07 | 0.00691 |
Table 1 assumes 100% e- mass of ‘9.11E-31 kg’, and h of 6.62607015E−34 j/s. Based on KE =mv, this suggests 4.26E-25 kgm/s flux per photon e-. Due to range of En values for elements, further models, experiments, and data analysis is required.
Table 2. Photon Electron / Sec Flux at Surface at 1000W/m2.
Photon Electron / Sec Flux Analysis Earths Surface 1000W/m2 |
Mass % of e- | 33% | 66% | 100% |
Mass of e- (kg) | 3.01E-31 | 6.01E-31 | 9.11E-31 |
Photons/m^2 | 6.65E+27 | 3.33E+27 | 2.20E+27 |
Photons/cm^2 | 6.65E+23 | 3.33E+23 | 2.20E+23 |
Photons/nm^2 | 6.65E+09 | 3.33E+09 | 2.20E+09 |
Photons/pm^2 | 6,653.15 | 3,326.57 | 2,195.54 |
Photons/Watt | 6.65E+24 | 3.33E+24 | 2.20E+24 |
% Diff from Previous | 212,560.58 | 106,280.29 | 70,144.99 |
Due to the challenge of quantifying how many photons, electrons vs O2/N2 molecules in orbit and Earth’s surface, further research may quantify photons vs electron density, velocity, flux, etc. This approach can be developed to other planetary bodies and is further discussed in next section.
3.2. Planetary Photon Electron Radiation Fluxes
Table 3. Solar Flux Planets in Solar System.
Solar Flux Planets in Solar System |
| Mercury | Venus | Earth | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Neptune | Uranus | Pluto |
Solar Flux above Atmosphere (W/m2) | 8,750 | 2,857 | 1,400 | 622 | 52 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
Surface Area (106 km2) | 74.8 | 460.2 | 510.1 | 144.4 | 61420 | 42700 | 8083 | 7618 | 17.7 |
Surface Area (m2) | 7.48E+13 | 4.60E+14 | 5.10E+14 | 1.44E+14 | 6.14E+16 | 4.27E+16 | 8.08E+15 | 7.62E+15 | 1.77E+13 |
# of Photons/m2 @ 30% e- mass | 7.83E+28 | 2.56E+28 | 1.25E+28 | 5.57E+27 | 4.65E+26 | 1.34E+26 | 3.58E+25 | 1.79E+25 | 8.95E+24 |
# of Photons/m2 @ 70% e- mass | 3.36E+28 | 1.10E+28 | 5.37E+27 | 2.39E+27 | 1.99E+26 | 5.75E+25 | 1.53E+25 | 7.67E+24 | 3.84E+24 |
Photons Planet/Photons Earth 30% | 625% | 204% | 100% | 44% | 3.71% | 1.07% | 0.29% | 0.14% | 0.07% |
Photons Planet/Photons Earth 70% | 625% | 204% | 100% | 44% | 4% | 1% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
Tables 3 and 4 are based on solar flux (W/m
2) from (Matloff, et al, 2023). With n =Flux/mass*velocity, this would suggest Mars and Venus have 44% and 204% number of photons or electrons per m
2 at top of atmosphere compared to Earth.
Table 4. Planetary Flux from Electrons in Atmospheres.
Theoretical Planetary Flux from Electrons in Planet Atmospheres (W/m^2) |
% electron of Atmosphere Flux | Mercury | Venus | Earth | Mars | Jupiter | Saturn | Neptune | Uranus | Pluto |
Solar Flux above Atmos (W/m2) | 8,750 | 2,857 | 1,400 | 622 | 52 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
1.00% | 87.5 | 28.57 | 14 | 6.22 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
5.00% | 437.5 | 142.85 | 70 | 31.1 | 2.6 | 0.75 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
10.00% | 875 | 285.7 | 140 | 62.2 | 5.2 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
20.00% | 1750 | 571.4 | 280 | 124.4 | 10.4 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
30.00% | 2625 | 857.1 | 420 | 186.6 | 15.6 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
40.00% | 3500 | 1142.8 | 560 | 248.8 | 20.8 | 6 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
Table 4 outlines solar flux above atmosphere and % range of flux hypothetically reaching planet’s surface. Model excludes atmospheric height and assuming constant particle velocity. Percent of flux from electrons can be computed to account for radiation flux from higher mass elements such as hydrogen, helium, beta, and gamma rays. The planetary flux analysis and data help advance models of space systems, solar panels in orbit of planets and on surface of planets. Future analysis correlates photon electrons with surface and atmosphere temperature, altitude, E and B-field gradients.
3.3. Light Absorption in Skin & Sunlight Vitamins
As EM fields related to light and have effects on biology, photobiomodulation (PBM) with red and near-infrared (IR) light has beneficial effects in animal models of diseases.
| [12] | Heiskanen, V., Pfiffner, M., & Partonen, T. (2020). Sunlight and health: shifting the focus from vitamin D3 to photobiomodulation by red and near-infrared light. Ageing research reviews, 61, 101089. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101089 |
[12]
. UV is an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength from 10-400 nm, corresponding to penetration depth between 20-150 μm in human skin
| [13] | Merve et al "Wavelength-dependent penetration depths of ultraviolet radiation in human skin," J. Biomed. Opt. 13(4) 044030 (1 July 2008) https://doi.org/10.1117/1.2957970 |
[13]
. Visible red wavelengths 600-700 nm red light — can absorb 4-5mm into the skin. Moreover, Cytochrome c oxidase (CYP), absorb infrared light near the unit IV respiratory chain mitochondria
| [14] | Dompe, C., et al. (2020). Photobiomodulation—Underlying Mechanism and Clinical Applications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1724. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061724 |
[14]
and could absorb wavelengths of electromagnetic spectrum to produce ATP. Moreover, Vitamin D and other vitamins are synthesized in mammalian skin in skin keratinocytes through the absorption of UV and IR photons or electrons. Where photolysis helps to oxidize, break B-ring and re-orient covalent pairs of two e- in C-C single bonds (154pm) and forms two double C=C bonds (134 pm) on second ring structure of pre-D3, which can further be photolysed.
Figure 7. Light Acting on Pre-vitamin D3 where 2-electron covalent bonds are re-oriented and relocated.
Local e- deposition is a function of e- volume to valence and covalent e- charge ratio, and radian interatomic pauli repulsion forces (∇FP) between e- orbitals for bond alignment geometry. With temperature of <5,772 K at solar surface, IR and Visible wavelengths are radiated outward, based on E=hc/lambda, a 645 nm particle would have 1.92eV energy per ‘photon’ or electron, where 1eV = 1.6E-19J, if traveling at C=3E8 m/s. Further KE analysis may be based on average translational kinetic energy (KE (eV) = 3/2kT) and Stefan-Boltzmann (SB) equation. KE=3/2kT suggests 0.7598 eV energy released for reactions at 5600K at Solar surface.
As Pressure/Area = F, where F is flux in w/sq m, Planck Radiation Law also quantifies energy radiated where s= 5.67 x 10
-8 Joule/ (m
2sec K
4). Considering every reaction has an equal and opposite reaction based on Newton’s Third Law of Motion, this effect is further demonstrated from Compton Scattering and Photoelectric effect, where electrons are ejected or scattered from matter and irradiated sample volume can be calculated. With photon flux and radiation correlated to eV and mass, some sources suggest solar wind has 4-12 N/cm3 (9 n/cm3) with average 2.05E-3 W/m^2 in particle energy and 6.2 B Field and 1.7E-13 W/m^2 magnetic energy density outlined from
| [18] | Lutz, 2024. "Planetary and Solar Electromagnetic Lensing (SEL), Geometry, Astrophysics for Exoplanet Imaging," AIAA 2024-4925. AIAA ASCEND 2024. July 2024. https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2024-4925 |
[18]
.
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantum Mechanics
With +½ or -½ opposite angular spin charge states, negative photons are fragments derived from electrons with opposite spin charge. Photons of different sizes have masses and spin magnetic moments with negative photon velocity shift ~0.0295 ppm.
| [16] | PAS Rochester. (n.d.). Starlight and Blackbodies. Radiation Laws. |
[16]
Electron orbiting a proton in H are observed to travel at 1/137c or 2,190km/s, which would be correlated to E
n and KE flux difference.
rcos2(t), rsin2(t), rsin2(t) = r2(11)
∇F= δ/dt[rcos2(t), rsin2(t), rsin2(t)] (12)
Curl is the rate of change or rotation of vector field, defined as cross product of length that corresponds to the speed of the rotation. A vector field has a curl of zero if it does not exhibit any rotational behavior around point.
4.2. Red Shift and Tired Light
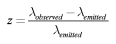 (13)
(13) Astronomers use spectroscopy to measure redshift, which is believed to have higher accuracy considering current velocity ranges. A redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and reduces or stretches the frequency. Doppler Effect and Tired Light model also suggest light loses energy with time, distance, and collision, with Tired Light proposed in 1929 by Fritz Zwicky. After Einstein proposed light quanta in 1905 and Relativity, Arthur Compton published a paper In 1923, verifying derivation (λ’-λ =h/m
ec)(1-cosθ), where m
e is e- rest mass, c is velocity of particle, theta is scattering angle, and h is plancks constant. H/m
ec is also compton wavelength of e-, as CODATA 2022 value is generally considered at ~ 2.43E-12 m
.
Planetary and Solar Electromagnetic Lensing (SEL) was recently discovered by K. Lutz which opposes solar gravitational lensing (SGL). SEL/PEL better characterizes ions flowing the plasma wake around a body to converge at magnetic reconnection focal point.
At solar reconnection point 100 to 200 Re downtail (e.g., Walker et al. 1999), orders of magnitude more photons. As Earth accelerates e- as an electron accelerator
, research suggests photons or electrons have charge.
4.3. Electromagnetic Quanta Scattering (EQS)
The Electromagnetic Quanta Scattering (EQS) model is first outlined and derived by Kole Lutz in 2024 where EQS Curl Vector (∇xF) models magnitude change in circulation density and flux density vector of Quanta and EM Quanta Divergence (EQD) Model. EQS and EQD may be used to characterize absorption/emission events, and to characterize quanta wave e- fragments ejected.
Figure 9. EQS Curl Model of Quanta in Motion around Electron.
where Figure a) above suggests angular velocity vector of particles coupling or converging in Z/ZY plane or or ρ, θ, φ or nearest neighbor in rad/sec or deg/sec. If θQ-Scatter > 180 or θscatter as highlighted in Figure b, this may suggest a quanta e- radiated in similar direction of B-field or E-field. EQS and EQD Model would be correlated with electric and magnetic field intensities outlined in Equation:
where Q=Q/is quanta volume density and F= Q = mV.
where Fb is magnetic field force and N is coil turns.
As greater turns in a wire generates higher radiated energy, this may suggest e- quanta overlap density with tighter wraps that increase micro Tesla. When electrons collide at angles with EMI, scattered quanta is emitted via EM radiation with collisions in XX, YY, ZZ axis and other spin axis. With up to 4.68E14 nm/sec spin, every one collision suggests cascade of electrons are more perpendicular to flow, where valence electrons are most susceptible.
1(t) = -ω rsin(ωt+ φ) (18)
(19)
Wave Equation above outlines Ψ quanta velocity with x, y, z vector cross product. Following absorption-emission events in gas medium, electron- quanta particles.
J=L+S (20)
change in mass m of electron (Ψe) is inversely correlated with E (mV/m) and B Field (G) magnitude flux density.
J(edge)(t)/JQ(t)=JOffSpin Ratio(21)
where average Angular momentum (J) spin near e- cloud edge and Quanta scattered suggest off spin ratio correlated with dt during decoupling-scattering.
Figure 10. Potential Relationships between e- Quanta.
S(E) = -dE/dx -dE/dy-dE/dz(22)
As particles collide with medium, the deposited energy can be obtained by taking derivative of the entire path length of the ion of E and B-field. Stopping power S(E) equal to the loss of energy E per unit path length. As ~ velocity, KEx KEy KEz of radiated quanta is modeled by deposited energy or irradiance loss. As particles slow down to rest, less magnitude of vector near each axis suggests minimal quanta scattered or radiation loss, whereby the electron quanta would be maximally coupled. In approaching maxima of wave, scatterer would have > V or ∂x/∂t or ∂KE.
Future experiments in a lab that may require funding may quantify electron mass, spin charge, and velocity’s with single photon detectors (e.g., TES, KIDs, SNSPDs, SQUIDs, and bolometers). In summary, the Electromagnetic Quanta Scattering (EQS) Model may be used to characterize absorption/emission events, and to characterize quanta wave e- fragments ejected.
5. Conclusions
Research holds potential to improve weather and climate models and to quantify e- interactions in atmosphere, to characterize absorption spectra, and light flux from stars.
Photon Electron / Sec Flux Analysis Earth’s Surface suggests 2 to 6.65x1024 photon electrons/watts at 100-33% electron mass.
Incoming Photons as electron flux helps to characterize and improve accuracy of redox reactions and photosynthesis rates
Research improves physics, weather climate models, power systems (PV Cells, detectors, etc.), and materials across a variety of fields
Research holds potential to increase instrument sensitivity for Earth & planetary science, fundamental physics & biological research, laser communication, and astrophysics.
Abbreviations
ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
ADP | Adenosine Diphosphate |
EM | Electromagnetic |
ETC | Electron Transport Chain |
EQS | Electromagnetic Quanta Scattering |
EQD | Electromagnetic Quanta Divergence |
eV | Electron Volts |
IR | Infrared |
KE | Kinetic Energy |
NAIs | Negative Air Ions |
SEL | Solar Electromagnetic Lensing |
UV | Ultraviolet |
Acknowledgments
Author K. Lutz thanks friends and family and MPU University and Magneto Space for helping sustain research. The authors confirm this material or similar material has not been published in any other publication.
Author Contributions
Kolemann Lutz is the sole author. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work is not supported by any external funding. There are no conflicts of interest to report and no competing financial interests exist.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the outcome of this research work has been reported in this manuscript. The data is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and no competing financial interests.
References
| [1] |
Feldman, 1998. FIP Effect in the Solar Upper Atmosphere: Spectroscopic Results. Space Science Reviews 85, 227–240 (1998).
https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005146332450
|
| [2] |
Zuccaro, D. E., "Analysis of the Simulation of the Solar Wind," ASTM/IES/AIAA Space Simulation Conference, 14-16 Sept 1970.
|
| [3] |
Siegel, E. (2022, October 12). The Sun’s energy doesn’t come from fusing hydrogen into helium (mostly). Forbes.
|
| [4] |
Bommier, Véronique. (2020). Solar photosphere magnetization. Astronomy & Astrophysics. 634.
https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201935244
|
| [5] |
Lutz, 2024. Absorption and Emission Spectra Correlated with Ejected Quasi-Electrons, March 2024, ResearchGate
|
| [6] |
Jiang, S. Y., et al (2018). Negative Air Ions and Their Effects on Human Health and Air Quality Improvement. International journal of molecular sciences, 19(10), 2966.
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102966
|
| [7] |
Lutz, et al, 2024. Electromagnetic Fields to Sustain Life on Earth and Beyond, 72nd International Astronautical Congress (IAC) At: Dubai, October 2021.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/356474843_Electromagnetic_Fields_to_Sustain_Life_on_Earth_in_Space_and_Planets
|
| [8] |
Harrison R. G., Carslaw K. S. Ion-aerosol-cloud processes in the lower atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003; 41
https://doi.org/10.1029/2002RG000114
|
| [9] |
Goto, et al. Property changes in materials due to atomic oxygen in the low Earth orbit. CEAS Space J 13, 415–432 (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12567-021-00376-2
|
| [10] |
Banks, Bruce & Miller, Sharon & de Groh, Kim. (2004). Low Earth Orbital Atomic Oxygen Interactions With Materials. NASA TM-220042213233. 2.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2514/6.2004-5638
|
| [11] |
Rowe, Leonard, Effect of Sunlight On the Corrosion of Steel. Journal of Corrosion (1961) 17(6): 267t–268t.
https://doi.org/10.5006/0010-9312-17.6.93
|
| [12] |
Heiskanen, V., Pfiffner, M., & Partonen, T. (2020). Sunlight and health: shifting the focus from vitamin D3 to photobiomodulation by red and near-infrared light. Ageing research reviews, 61, 101089.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101089
|
| [13] |
Merve et al "Wavelength-dependent penetration depths of ultraviolet radiation in human skin," J. Biomed. Opt. 13(4) 044030 (1 July 2008)
https://doi.org/10.1117/1.2957970
|
| [14] |
Dompe, C., et al. (2020). Photobiomodulation—Underlying Mechanism and Clinical Applications. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(6), 1724.
https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9061724
|
| [15] |
Schofield JT, Taylor FW. Net global thermal emission from the Venusian atmosphere. Icarus. 1982; 52(2): 245–262.
https://doi.org/10.1016%2F0019-1035(82)90111-7
|
| [16] |
PAS Rochester. (n.d.). Starlight and Blackbodies. Radiation Laws.
|
| [17] |
Yuan, Daocheng & Liu, Qian. (2021). Photon energy and photon behavior discussions. Energy Reports. 8.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.11.034
|
| [18] |
Lutz, 2024. "Planetary and Solar Electromagnetic Lensing (SEL), Geometry, Astrophysics for Exoplanet Imaging," AIAA 2024-4925. AIAA ASCEND 2024. July 2024.
https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2024-4925
|
| [19] |
Livingston, 2004. Sun, Energy from. Encyclopedia of Energy, Elsevier, Pages 777-788,
https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-12-176480-X/00049-8
|
| [20] |
CODATA 2022 value for Compton wavelength for the electron from NIST.
https://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?ecomwl
|
Cite This Article
-
-
@article{10.11648/j.ijass.20251301.12,
author = {Kolemann Lutz},
title = {Sunlight Photons Made of Electrons from Stars
},
journal = {International Journal of Astrophysics and Space Science},
volume = {13},
number = {1},
pages = {11-20},
doi = {10.11648/j.ijass.20251301.12},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijass.20251301.12},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.ijass.20251301.12},
abstract = {From the 1900s to 2020s, humans believed photons were massless particles. However, solar wind is made of ionized particles such as hydrogen and helium stripped of electrons. This study is one of the first to identify photons as electrons based on analysis with photosynthesis, oxidation reduction reactions, ionization energy, vertical electric fields, and negative air ions (NAIs), when O2 combines with electron to form O2-. Earth's electrical field is around 100-300 V/metre which further suggests charge is due to light photons or electrons. Electron kinetic and ionization energies of both electrons (e-) and photons are analyzed. A photon electron radiation flux analysis across each planetary body also quantifies photons/m2, which helps to advance systems and models in orbit and at surface of planets. After first discovery of photons as electrons from Kole Lutz in 2024, research helps to quantify electron interactions, absorption/emission to improve weather climate models, photosynthesis, power systems (PV Cells, detectors, etc.), corrosion redox reactions, and materials across a variety of fields from energy, communication to biology and space systems. Research holds potential to increase instrument sensitivity for Earth and planetary science, physics, lasers, communication, and to characterize absorption spectra, and light flux from stars.
},
year = {2025}
}
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
-
TY - JOUR
T1 - Sunlight Photons Made of Electrons from Stars
AU - Kolemann Lutz
Y1 - 2025/02/25
PY - 2025
N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijass.20251301.12
DO - 10.11648/j.ijass.20251301.12
T2 - International Journal of Astrophysics and Space Science
JF - International Journal of Astrophysics and Space Science
JO - International Journal of Astrophysics and Space Science
SP - 11
EP - 20
PB - Science Publishing Group
SN - 2376-7022
UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijass.20251301.12
AB - From the 1900s to 2020s, humans believed photons were massless particles. However, solar wind is made of ionized particles such as hydrogen and helium stripped of electrons. This study is one of the first to identify photons as electrons based on analysis with photosynthesis, oxidation reduction reactions, ionization energy, vertical electric fields, and negative air ions (NAIs), when O2 combines with electron to form O2-. Earth's electrical field is around 100-300 V/metre which further suggests charge is due to light photons or electrons. Electron kinetic and ionization energies of both electrons (e-) and photons are analyzed. A photon electron radiation flux analysis across each planetary body also quantifies photons/m2, which helps to advance systems and models in orbit and at surface of planets. After first discovery of photons as electrons from Kole Lutz in 2024, research helps to quantify electron interactions, absorption/emission to improve weather climate models, photosynthesis, power systems (PV Cells, detectors, etc.), corrosion redox reactions, and materials across a variety of fields from energy, communication to biology and space systems. Research holds potential to increase instrument sensitivity for Earth and planetary science, physics, lasers, communication, and to characterize absorption spectra, and light flux from stars.
VL - 13
IS - 1
ER -
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download

 (13)
(13)