Abstract
This research is based on the panel data from the annual reports of Chinese commercial banks for the years 2010-2020. A panel data model is constructed to empirically investigate the influence of commercial banks' asset allocation on financial stability. The study innovatively explores the differences between large-scale banks and general-scale banks in this context, as well as the interaction effects between large-scale banks and their methods of capital application. The findings indicate that: firstly, the higher the proportion of corporate loans in commercial banks, the stronger the stability. With the support of national policies, the operating environment for emerging industries has improved, leading to a reduction in bankruptcy risks and further decreasing the credit risk of related banks, which contributes to the enhancement of banks' financial stability. Additionally, compared to securities investments affected by market fluctuations, corporate loans are less susceptible to significant capital changes, and their risks are primarily determined by the operating conditions of the related enterprises, making them relatively controllable. Secondly, the higher the proportion of personal loans in commercial banks, the stronger the stability. The largest part of personal loans consists of housing mortgage loans, which have a low non-performing loan rate and high quality in China. Therefore, an increase in personal loans helps to enhance the financial stability of banks. Thirdly, large-scale banks exhibit lower financial stability. Due to the redundancy in management personnel in large-scale banks, management costs, adjustment costs, and transaction costs are relatively high. Furthermore, it is worth noting that because large-scale banks hold a significant amount of surplus funds, they are prone to excessive securities investments. Fluctuations in the securities market increase external risks and decrease financial stability.
Keywords
Commercial Banks, Asset Allocation, Financial Stability, Asset Size, China
1. Introduction
Since China's accession to the World Trade Organization in 2001, its financial industry has officially embarked on a path of opening up. In 2006, China introduced relevant legal policies aimed at attracting foreign banks. From 2007 to the present, China's financial institutions have been engaged in a deepening reform process centered on risk prevention, ensuring soundness, and capital market development. In August 2018, to further expand the opening up of the banking industry, the China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission abolished the foreign ownership restrictions on domestic banks and financial asset management companies, implementing a consistent equity investment ratio rule for both domestic and foreign capital. These measures to open up the financial market have injected new vitality into the financial industry and provided opportunities for Chinese financial institutions to introduce advanced management methods for asset allocation and stability improvement.
However, after 2011, due to the slowdown of domestic economic growth and an increase in corporate bankruptcies, the non-performing assets of Chinese commercial banks continued to rise.
Looking at the broader environment of commercial banks over the past decade, the banking industry is undergoing significant market changes. In recent years, the banking industry has been greatly affected by online banking and interest rate liberalization. The traditional operation of Chinese commercial banks, which relies heavily on deposit and loan interest rates, is almost impossible to adapt to today's financial market. Therefore, in order to break free from the current predicament, commercial banks must not remain passive but continuously improve and update their business models, innovating their commercial systems in line with the trends of the times. The maturity of commercial banks' asset allocation is an important indicator of the maturity of commercial banks and a key measure of whether the banking industry is adapting to modern development. Under the current global economic situation, many overseas banks are continuously optimizing the use of funds and actively adjusting the proportion of various allocation methods to improve their development environment.
In the continuously evolving world economic system and with the development of economic globalization, many large foreign banks have also participated in the competition of the domestic banking industry. At the same time, the development of digital finance in recent years has also greatly impacted the traditional banking industry. Coupled with the increased level of openness of China's financial market, foreign financial institutions are also participating in the competition in China's banking industry. Under the dual pressures of digital finance and financial openness, China's commercial banks must withstand the dual pressures of foreign banks and digital finance, and the competition in the industry is very fierce. Therefore, in order to promote the development of commercial banks and optimize asset allocation methods and improve industrial structures, it is a trend. Strengthening the risk management of asset allocation, improving the efficiency of asset use, and optimizing the structure of asset allocation are important contents for Chinese commercial banks to manage their assets.
By the end of 2020, the total assets of China's large state-owned banks have all exceeded one trillion. As a crucial part of China's economy and finance, how should the huge amount of funds controlled by banks be used more efficiently? Should large-scale banks and general joint-stock commercial banks allocate assets differently? These questions do not have a unified conclusion in academia. Moreover, with the maturation of the financial system and the development of the national economy, the size of banks will inevitably continue to rise, and trillion-level banks will gradually increase. To cope with the changes in the external economic environment, the optimal asset allocation methods for these large-scale banks will inevitably differ from those of ordinary commercial banks. This study aims to use panel data from various commercial banks to analyze the impact of various asset allocation methods on financial stability, verify whether differences in bank size will cause differences in stability, and specifically how the interaction between bank size and asset allocation affects financial stability, exploring the optimization direction and management focus of bank asset allocation structures.
This study mainly analyzes the impact of commercial banks' fund allocation on their financial stability; whether there are differences in the impact of asset allocation on financial stability according to the size of the bank; if there are differences, what are the reasons for these differences, and whether the interaction between large-scale banks and fund allocation methods has an impact on financial stability is also a research goal of this study.
Although there are related studies on fund allocation and financial stability in existing literature, this study distinguishes itself by using bank asset size as a criterion to analyze the differences between large-scale banks and ordinary joint-stock commercial banks on this issue. Furthermore, it analyzes whether the interaction between large-scale banks and fund allocation methods has an impact on financial stability. On this level, the study has its innovativeness compared to existing research. At the same time, this study uses panel data analysis to make up for the shortcomings of traditional cross-sectional data analysis and time series analysis, analyzing both cross-sectional and time series data, which is more in line with the actual characteristics of bank fund allocation.
2. Literature Review
Banks primarily deploy the capital they raise to extend loans, with a substantial remainder allocated to securities investments. According to Naehwang Lee
| [1] | Naehwang Lee. The Impact of Changes in Domestic Banks' Funding and Operational Structure on Profitability after the Financial Crisis. Ph. D. Thesis, Kyunghee University, 2015. |
[1]
, loans serve as the principal revenue-generating instruments for commercial banks and are classified by borrower type into personal loans, corporate loans, and public or other loans. The academic consensus holds that diversification of the loan portfolio is advantageous for bolstering banks' profitability. However, a countervailing view suggests that such diversification may intensify banking risks.
Saunders and Cornett
| [2] | Saunders, A. and M. Cornett. Financial Institutions Management, McGraw Hill. 2003. |
[2]
contend that loan diversification is conducive to bolstering efficiency and profitability within the banking sector. Acharya et al., in their work
| [3] | Acharya, V., I. Hasan, and A. Saunders. Should Banks be Diversified? Evidence from Individual Bank Loan Portfolios. Journal of Business. 2006, 32, 1355-1412. https://doi.org/10.1086/500679 |
[3]
, posit that specialization in loans to specific industries not only enhances banks' profitability but also mitigates risk. They argue that such specialization allows banks to leverage industry-specific knowledge, potentially leading to better risk assessment and pricing strategies. Concurrently, they acknowledge that a diversified loan portfolio, while intensifying competition among banks, may also heighten risk due to the broader exposure to various sectors.
In a similar vein, Steve Beck and Tim Ogden
| [4] | Steve Beck, Tim Ogden. Beware of Bad Microcredit. Harvard Business Review. 2007, 85(9), 20-22. |
[4]
identify small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) loans as an emerging business frontier for financial institutions, including banks. They suggest that tapping into the SME market presents new opportunities for growth and diversification. However, they caution that the inherent characteristics of SMEs, such as their smaller scale and often lower credit ratings, necessitate careful management of non-performing loans to avoid exacerbating credit risk.
Regarding personal loans, the academic community generally considers them a stable asset. The Sichuan Regulatory Bureau of the China Banking Regulatory Commission in reference
| [5] | China Banking Regulatory Commission Sichuan Regulatory Bureau Research Group, Wang Jun Quan. Research on the Adjustment Strategy of Bank Credit Structure under the Background of Economic Transformation - A Case Study of Sichuan. Southwest Finance. 2012(07), 7-11. |
[5]
believes that commercial banks should adapt to the current trend of increasing personal loans in the credit structure and vigorously develop personal loans to diversify credit concentration. However, certain scholars recommend moderating the share of personal loans, with a particular emphasis on mortgages, advocating for the strategic allocation of scarce credit resources towards high-quality enterprises and industries. This approach aims to enhance industry-specific credit concentration, as suggested by Du Tao
and Gao Xueting
| [7] | Gao Xue Ting. Thoughts on the Adjustment of Commercial Bank Credit Structure. Hebei Finance. 2012, (07), 33-34. |
[7]
. Lee in reference
analyzed the relationship between personal loans and the financial robustness of South Korean commercial banks. The results show that there is no significant correlation between the proportion of personal loans in banks and the financial robustness of banks. However, the relationship between personal loans and financial robustness changed before and after the financial crisis, with a positive shift occurring after the crisis. The study points out that since the 2008 financial crisis, with the increase in personal loans, the financial robustness of banks has improved. Kim et al. in reference
| [9] | Kim Hyun-jung, Son Jong-chil, Lee Dong-ryul, Lim Hyun-jun, and Na Seung-ho. Analysis of the Causes of Household Debt Increase and Sustainability in Our Country. Bank of Korea Economic Review. 2013(8), 1-52. |
[9]
found that personal loans in South Korean commercial banks are centered around high-income groups and increase with asset purchases, making them a relatively safe way of utilizing assets. They call for more attention to personal loans that maintain livelihoods and suggest increasing the proportion of loans from non-bank financial institutions.In reference
| [10] | Huang Zi Xin and Bae Soo Hyun. A Study on the Effect of Household Loans on Financial Soundness in Banks. The Journal of the Convergence on Culture Technology (JCCT). 2021, 7(4), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.17703/JCCT.2021.7.4.1 |
[10]
, Huang Zixin and Bae Soo-Hyun conducted a study on the financial stability of South Korean commercial banks, utilizing panel data from 2007 to 2018. Their findings indicate that post-financial crisis, an increased ratio of residential mortgage loans in these banks has been instrumental in improving their capital adequacy ratio, thus effectively enhancing financial robustness. The study posits that, in the face of external changes including fluctuations in the international financial environment and declines in asset values, commercial banks should concentrate on fostering the healthy and stable progression of personal loans.
Regarding corporate loans from banks, numerous studies have been conducted worldwide. Kang Taek-ho
| [11] | Kang Taek-ho. The Current Status of Banknote Issuance: A Case Study. Finance. 1995(7). |
[11]
suggests that when market real interest rates show a stable downward trend, banks can increase lending by adjusting their asset portfolios. Moreover, during periods of economic prosperity, commercial banks tend to operate the funds they raise in the form of loans. He also suggests expanding the loan scale of commercial banks by increasing their capital. Steve Beck and Tim Ogden
| [4] | Steve Beck, Tim Ogden. Beware of Bad Microcredit. Harvard Business Review. 2007, 85(9), 20-22. |
[4]
suggest that SME loans are a new performance growth point for financial institutions like banks. However, given the small size, low credit level, and other factors of SMEs, they recommend careful handling of non-performing loans related to SMEs. Xu Heng
| [12] | Xu Heng. Design of Credit Management Plan for Micro and Small Enterprises Loan. Master's Thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2009. |
[12]
advocates actively developing SME loans. To address the high risk and high cost problems faced by financial institutions in SME loans, he proposed a series of internal control rules such as special management, separate accounting, and separate assessment for SME loans. Yuan Gang and Liu Huifeng
| [13] | Yuan Gang, Liu Hui Feng. A Brief Discussion on the Credit Risk Management of Banks to SMEs in China. Shanghai Finance. 2010(07), 89-91. |
[13]
propose that effectively assessing and managing the credit risk of SMEs is a problem that Chinese commercial banks must solve. They have found an applicable credit risk measurement model for Chinese SMEs through empirical research and advise commercial banks to pay attention to the credit risk management of SMEs.
Research on bank securities investment generally posits that such investment is beneficial for enhancing profitability. However, there is also evidence suggesting that securities investment may potentially increase banking risk. Generally speaking, financial assets have the inherent attribute of "high risk-high return." In terms of asset allocation, securities are volatile assets whose market value changes at any time. Although the risk is higher than loan assets, the return is also relatively higher. From this perspective, when banks invest in high-risk securities, they can expect corresponding high returns. In other words, banks with a higher proportion of securities in their asset allocation, in their business strategy, focus more on improving profitability rather than expanding loans. NaeHuang Lee
| [1] | Naehwang Lee. The Impact of Changes in Domestic Banks' Funding and Operational Structure on Profitability after the Financial Crisis. Ph. D. Thesis, Kyunghee University, 2015. |
[1]
found that South Korean commercial banks suffered from the global financial crisis, leading to a reduction in securities investments and a subsequent decrease in profitability.Xu Shuying
| [14] | Xu Shuying. Research on the Impact of Bond Investment on Commercial Bank Risk Taking. Review of Financial & Technological Economics. 2023(03), 68-87. |
[14]
conducted an empirical study on the impact of bond investment activities on banks' risk-taking. The study demonstrates that securities investment is conducive to increasing bank profitability and reducing the volatility of earnings, thereby diminishing the bank's risk exposure. Bai Yun
| [15] | Bai Yun. A Preliminary Discussion on the Innovation of Commercial Bank Financial Investment Business. Times Finance. 2016(33), 91-92. |
[15]
studied the current situation of domestic bank securities investments in China and suggested that due to unclear classification by regulatory personnel, the efficiency of domestic commercial banks' securities investment business has been reduced, increasing bank risk. Xu Yan
| [16] | Xu Yan. Analysis of the Risk of Commercial Bank Bond Investment under the New Normal. Business News. 2020(05), 82. |
[16]
showed that as China's economic development enters a new stage, the risk of commercial bank securities investments will increase. Therefore, domestic banks should improve their ability to identify and manage risks. However, currently, Chinese small and medium-sized commercial banks have a lower sensitivity to financial risks, have a shorter time in the financial market, especially the bond market, and interest rate fluctuations pose a significant threat to them.
In conclusion, a spectrum of opinions exists among researchers regarding the impact of securities investments on bank risk. Scholars like Bai Yun
| [15] | Bai Yun. A Preliminary Discussion on the Innovation of Commercial Bank Financial Investment Business. Times Finance. 2016(33), 91-92. |
[15]
and Xu Yan
| [16] | Xu Yan. Analysis of the Risk of Commercial Bank Bond Investment under the New Normal. Business News. 2020(05), 82. |
[16]
express concerns that such investments could potentially elevate bank risks. On the other hand, personal loans are widely regarded as a safer asset utilization method, as assessed by Kim Hyun-Jung et al.
| [9] | Kim Hyun-jung, Son Jong-chil, Lee Dong-ryul, Lim Hyun-jun, and Na Seung-ho. Analysis of the Causes of Household Debt Increase and Sustainability in Our Country. Bank of Korea Economic Review. 2013(8), 1-52. |
[9]
and Lee
. In contrast, the consensus on corporate loans tends to highlight their higher risk profiles, which are believed to negatively affect the financial robustness of banks. To address the challenges of high risk and cost associated with corporate loans, researchers, including Xu Heng
| [12] | Xu Heng. Design of Credit Management Plan for Micro and Small Enterprises Loan. Master's Thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2009. |
[12]
, propose the development and enhancement of credit management systems to improve risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
3. Materials and Methods
The bank data used in this study are based on the annual data from the top ten commercial banks from 2010 to 2020, manually collected from the banks' publicly released annual reports. Macroeconomic indicators are obtained by collecting and organizing data publicly released by the National Bureau of Statistics of China. The sample banks include ten large-scale commercial banks (Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China, Bank of Communications, Guangfa Bank, Shanghai Pudong Development Bank, CITIC Bank, Industrial Bank, and China Minsheng Bank). The study uses the financial data of the above banks to construct a panel data model for analysis, which simultaneously considers cross-sectional and time-series dimensions, and further divides the data into large-scale banks and non-large-scale banks for research. As of 2020, there are six trillion-level large-scale banks in China. Since the Postal Savings Bank of China has a different business model and bank characteristics from general banks, this study excludes the Postal Savings Bank and includes the five trillion-level commercial banks (Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China, and Bank of Communications) as the large-scale banks in the research object; the remaining 12 national joint-stock banks, this study selects 5 banks (Guangfa Bank, Shanghai Pudong Development Bank, CITIC Bank, Industrial Bank, and China Minsheng Bank) with easily accessible data as the non-large-scale bank samples. The different scales of the two groups may lead to differences in financial stability, which is also one of the important topics of this study.
The study uses the Expected Default Frequency (EDF) as the financial stability indicator of banks, which is calculated as the sum of asset return rate and equity ratio divided by the standard deviation of asset return rate, as provided in the study by Han Sang-seop and Lee Byung-yun
| [17] | Han Sang-seop and Lee Byung-yun. The Effects of Korean Banks' Funding Structure on Their Profitability and Management Stability. Korea Institute of Finance (KIF) Research Report. 2012(5), 1-89. |
[17]
. The Expected Default Frequency is commonly used to measure the distance to default of a company, and the higher the measurement value, the lower the possibility of the bank's bankruptcy. This study categorizes the methods of asset management into the proportions of corporate loans (CLP, Corporate Loan Proportion), personal loans (PLP, Personal Loan Proportion), and securities investments (SIP, Portfolio Investment Proportion). The proportion of corporate loans (CLP) in banks is measured by the share of corporate loans in total bank assets; the proportion of personal loans (PLP) in banks is measured by the share of personal loans in total bank assets; the proportion of securities investments (SIP) in banks is measured by the share of securities holdings in total bank assets.
Table 1. Definitions and Measurement Methods of Variables.
Variable Type | Variable Name | Measurement Method |
Dependent Variable | Expected Default Frequency (EDF) | (Asset Return + Equity Ratio)/Standard Deviation of Asset Return |
Concerned Variables | Corporate Loan Proportion (CLP) | Corporate Loans/Total Assets * 100 |
Personal Loan Proportion (PLP) | Personal Loans/Total Assets * 100 |
Securities Investment Proportion (SIP) | Securities Holdings/Total Assets * 100 |
Control variables | Interest Rate Spread (GAP) | Net Interest Income/Total Assets * 100 |
v | Bank Size (ASSET) | Natural Logarithm of Total Assets |
Consumer Price Index Growth Rate (CPI) | Year-on-year Growth Rate of Consumer Price Index |
GDP Growth Rate (GDP) | Year-on-year Growth Rate of Real GDP |
Dummy Variable for Large-Scale Banks (NB) | large-scale Bank 1, Non-large-scale Bank 0 |
Cross-Term Large Banks & Corp. Loans (NBCLP) | Dummy Variable * Corporate Loan Proportion |
Cross-Term Large Banks & Pers. Loans (NBPLP) | Dummy Variable * Personal Loan Proportion |
Cross-Term Large Banks & Sec. Inv. (NBSIP) | Dummy Variable * Securities Investment Proportion |
Control variables are selected to reflect the characteristics of bank finances and the macroeconomic environment, including the interest rate spread (GAP), bank size (ASSET), the growth rate of the Consumer Price Index (CPI), the growth rate of the House Price Index (HPI), and the growth rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Among them, the interest rate spread (GAP) is an indicator reflecting the degree of competition in the loan market and is often used to measure the economic conditions of bank loans. Jong Ku Kang
pointed out that with the intensification of market share competition, banks tend to lower loan interest rates and raise deposit interest rates, expanding their loan and deposit business scale by narrowing the interest rate spread. Bank size (ASSET) is measured by the natural logarithm of total bank assets. Boyd and Runkle
pointed out that bank size is inversely related to bank risk. The Consumer Price Index is commonly used as an indicator to measure inflation, and the degree of inflation will affect the level of bank risk, so the growth rate of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is selected as a control variable in this study. Since the fluctuation of the House Price Index is closely related to the risk level of bank loans, the growth rate of the House Price Index (HPI) is selected as a control variable. The growth rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a macroeconomic indicator measuring economic growth and plays a very important role in the asset management portfolio of commercial banks.
To investigate how banks' asset management affects financial risk and whether this impact varies with the state-owned nature of the banks, this study establishes Model (1). To explore the interactive effects between the state-owned bank dummy variable and the variables of interest, this study sets up Models (2), (3), and (4), and conducts panel data analysis. In this analysis, the dependent variables are the Return on Assets (ROA) and Expected Default Frequency (EDF), which serve as proxies for gauging the financial stability of banks. The variables of interest are operationalized through the proportions allocated to securities investments, personal loans, and corporate loans. Considering the additional effects over time, lagged variables of the first order are used for all independent variables.
Depending on the presence or absence of correlation between the individual effects and the independent variables, the Hausman test is used to select the more effective model between the fixed effects model and the random effects model. Since all models involved in this study contain dummy variables that do not change over time, the fixed effects model is used by default.
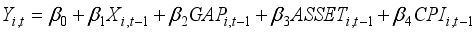
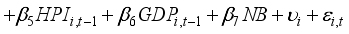 (1)
(1) 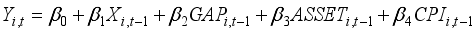
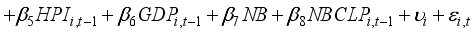 (2)
(2) 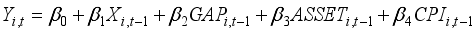
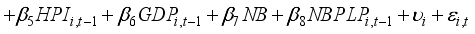 (3)
(3) 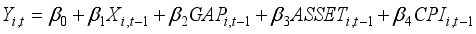
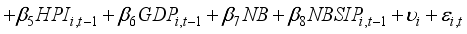 (4)
(4) 4. Results
Table 2. Description statistics of variables (unit:%).
Variable | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
EDF | 36.466 | 4.918 | 26.76 | 46.26 |
CLP | 34.038 | 6.315 | 20.89 | 50.41 |
PLP | 15.785 | 4.949 | 8.35 | 31.38 |
SIP | 24.270 | 8.560 | 7.26 | 54.13 |
GAP | 2.146 | 0.356 | 1.11 | 2.96 |
ASSET | 6.819 | 0.403 | 5.82 | 7.48 |
GDP | 7.836 | 1.373 | 5.95 | 10.64 |
CPI | 2.291 | 1.410 | -0.70 | 5.40 |
*Note: ASSET used the natural number of total assets.
Table 2 reports the descriptive statistics of various variables for Chinese commercial banks from 2010 to 2020. The average expected bankruptcy probability is approximately 36.47%, the average securities investment ratio is about 24.27%, the average personal loan ratio is around 15.79%, and the average corporate loan ratio is about 34.04%, which holds the largest proportion among the three types of fund allocation methods. The average net interest margin is about 2.15%, and the average natural logarithm of total assets is approximately 6.82. In terms of macroeconomic variables, the average growth rate of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is about 2.29%, and the average growth rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is about 7.84%, which are significantly higher than other Asian countries, reflecting the rapid economic development of China.
Table 3 shows the analysis results of the correlation between various variables in Chinese commercial banks. Looking at the relationship between corporate loans and bank stability, there is no significant result between the proportion of corporate loans and the expected bankruptcy probability. Regarding the relationship between personal loans and bank stability, there is a significant positive correlation between the proportion of personal loans and the expected bankruptcy probability. Looking at the relationship between the proportion of securities investment and bank stability, there is a significant positive correlation between the securities investment ratio and the expected bankruptcy probability.
Table 3. Analysis of the correlation.
| EDF | CLP | PLP | SIP | GAP | ASSET | GDP | CPI |
EDF | 1 | | | | | | | |
CLP | -0.10 (0.289) | 1 | | | | | | |
PLP | 0.49*** (0.000) | -0.5*** (0.000) | 1 | | | | | |
SIP | 0.20** (0.035) | -0.5*** (0.000) | 0.15 (0.126) | 1 | | | | |
GAP | -0.14 (0.158) | 0.33*** (0.000) | -0.4*** (0.000) | -0.4*** (0.000) | 1 | | | |
ASSET | 0.79*** (0.000) | -0.19** (0.049) | 0.27*** (0.005) | 0.30*** (0.002) | -0.02 (0.857) | 1 | | |
GDP | -0.5*** (0.000) | 0.63*** (0.000) | -0.7*** (0.000) | -0.5*** (0.000) | 0.42*** (0.000) | -0.4*** (0.000) | 1 | |
CPI | 0.03 (0.730) | 0.03 (0.794) | 0.01 (0.913) | -0.20** (0.040) | 0.31*** (0.001) | 0.01 (0.903) | 0.20** (0.035) | 1 |
*Note: Significant level*is 10%, ** is 5%, and *** is 1%.
The above correlation analysis only considers the simple correlation between the bank's financial characteristics without considering other factors. Therefore, to further clarify the relationship between fund allocation methods and bank stability, this study conducted panel data analysis.
Table 4 reports the results of the bank stability analysis. According to the analysis results of Model 1, the estimated impact of the proportion of corporate loans on stability is significantly positive at the 1% statistical level (+). That is, the higher the proportion of corporate loans in a bank, the stronger its stability. In other words, as the proportion of corporate loans increases, the financial stability of the bank increases accordingly. From a macroeconomic perspective, our country is in a period of rapid economic development. With the support of national policies, the survival environment of emerging industries has been greatly improved, which reduces the bankruptcy risk of companies and further reduces the credit risk of related banks, enhancing the financial stability of banks. On the other hand, compared with personal loans, corporate loans have larger individual transaction amounts and lower management costs per unit of money, which is beneficial for banks to retain profits and improve stability.
The estimated impact of the proportion of personal loans on stability is significantly positive at the 1% statistical level (+). That is, the higher the proportion of personal loans in a bank, the stronger its stability. Personal loans, with housing mortgages being the largest component, contribute to this stability.
The impact of the proportion of securities investment on stability does not show a significant value statistically. Therefore, it cannot be said that the proportion of securities investment in a bank has an impact on bank stability.
Table 4. The results of bank stability analysis.
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
coef. | P | coef. | P | coef. | P | coef. | P |
INTERCEPT | -48.023 | -3.9*** (0.000) | -53.424 | -5.0*** (0.000) | -47.749 | -3.7*** (0.000) | -51.496 | -4.3*** (0.000) |
CLP | 0.363 | 6.01*** (0.000) | -0.012 | -0.34 (0.737) | 0.356 | 5.56*** (0.000) | 0.340 | 5.61*** (0.000) |
PLP | 0.403 | 6.35*** (0.000) | 0.392 | 6.20*** (0.000) | 0.395 | 5.96*** (0.000) | 0.403 | 6.34*** (0.000) |
SIP | 0.001 | 0.02 (0.980) | 0.312 | 5.63*** (0.000) | 0.005 | 0.14 (0.886) | -0.001 | -0.00 (0.998) |
GAP | 0.512 | 0.64 (0.524) | 0.664 | 0.86 (0.390) | 0.564 | 0.69 (0.489) | 0.548 | 0.69 (0.490) |
ASSET | 10.575 | 6.57*** (0.000) | 11.600 | 8.05*** (0.000) | 10.482 | 6.10*** (0.000) | 11.101 | 6.92*** (0.000) |
GDP | -0.895 | -3.4*** (0.001) | 0.113 | 0.70 (0.486) | -0.842 | -3.1*** (0.002) | -0.778 | -2.8*** (0.006) |
CPI | 0.161 | 1.05 (0.293) | -0.779 | -2.9*** (0.004) | 0.151 | 0.98 (0.326) | 0.121 | 0.76 (0.446) |
DUM | -2.012 | -1.84* (0.066) | -7.746 | -2.07** (0.039) | -2.733 | -1.56 (0.119) | -0.150 | -0.07 (0.945) |
NBCLP | | | 0.134 | 1.44 (0.150) | | | | |
NBPLP | | | | | 0.058 | 0.60 (0.547) | | |
NBSIP | | | | | | | -0.102 | -1.05 (0.293) |

| Included | Included | Included | Included |
R-sq. Within | 0.774 | 0.768 | 0.775 | 0.773 |
N | 110 | 110 | 110 | 110 |
Random-effects | YES | YES | YES | YES |
It is worth noting that the relationship between the dummy variable for large-scale banks in this study and bank stability is significantly negative at the 10% statistical level (-). That is, there is a difference in financial stability between large-scale banks and non-large-scale banks, with large-scale banks having relatively lower financial stability. In other words, the larger the bank, the lower the financial stability. This is due to the relatively large number of management personnel in large-scale banks, with higher management, adjustment, and transaction costs. Chen Jingxue and Bie Shuangzhi
also put forward similar views in their research. In addition, large banks have more surplus funds, which may lead to an excess of securities investment. The fluctuation of the securities market will increase external risks and reduce financial stability. Hidayat et al.
| [21] | Wahyu Yuwana Hidayat, Makoto Kakinaka, Hiroaki Miyamoto. Bank risk and non-interest income activities in the Indonesian banking industry. Journal of Asian Economics. 2012. 23(4), 335-343. |
[21]
also reached similar conclusions in their research. They used bank data from 2001 to 2008 and found that the relationship between the bankruptcy risk of commercial banks and business diversification is related to bank size, and the business diversification of large-scale banks has more negative impacts.
The cross terms of the dummy variable for large-scale banks and various asset allocation methods in this study did not show a strong correlation statistically. Therefore, it cannot be said that the higher the proportion of corporate loans in large-scale banks, the higher the bank stability; it also cannot be said that the higher the proportion of personal loans in large-scale banks, the higher the bank stability; and it cannot be said that the higher the proportion of personal loans in large-scale banks, the higher the bank stability.
5. Discussion
This study primarily investigates the impact of commercial banks' fund allocation on their financial stability. It also examines whether there are differences in the impact of asset allocation on financial stability between large-scale banks and general commercial banks, as well as the interactive effects between large-scale banks and various fund allocation methods. Using the Expected Default Frequency (EDF) as the indicator of a bank's financial stability, the study categorizes asset management methods into the proportions of corporate loans, personal loans, and securities investments. The data from the top ten commercial banks from 2010 to 2020 are used to construct a panel data model that analyzes both cross-sectional and time-series aspects, and the data are further divided into large-scale banks and non-large-scale banks for research. The empirical analysis results are as follows:
Firstly, the proportion of corporate loans in banks has a significantly positive impact on stability at the 1% statistical level. That is, the larger the proportion of corporate loans in a bank, the stronger its stability. In other words, as the proportion of corporate loans in banks increases, the financial stability of the bank correspondingly improves. From a macroeconomic perspective, China is currently in a period of rapid economic development. With the support of national policies, the operating environment for emerging industries has greatly improved, reducing the risk of corporate bankruptcy and further decreasing the credit risk of related banks, thereby enhancing the financial stability of banks. On the other hand, compared to securities investments affected by market fluctuations and large capital changes, the risks of corporate loans mainly depend on the operating conditions of the related enterprises and are relatively controllable. The research by Du Tao
also supports the views of this study, suggesting that increasing the concentration of corporate loans helps improve the credit risk of banks. He recommends that banks enter policy-supported and market advantage industries and withdraw from declining industries, thereby optimizing the loan structure, improving bank loan assets, and reducing credit risk.
Secondly, the proportion of personal loans in banks also has a significantly positive impact on stability at the 1% statistical level. That is, the larger the proportion of personal loans in a bank, the stronger its stability. As personal loans increase, the financial stability of the bank correspondingly improves. The largest part of personal loans is housing mortgage loans. Chen Hongbo and Wang Zhen
conducted a comprehensive analysis of the financial risks of housing loans from the perspectives of bank loans, real estate companies, and homebuyers. Their research indicates that compared to international experience, the non-performing loan rate of China's real estate loans is low, and the quality of mortgage loans is high, which corroborates the results of this study.
Thirdly, it is worth noting that the relationship between the dummy variable for large-scale banks and bank stability is significantly negative at the 10% statistical level. That is, there is a difference in financial stability between large-scale banks and non-large-scale banks, with large-scale banks having relatively lower financial stability. In other words, the larger the scale of the bank, the lower its financial stability. This is because large-scale banks have a relatively large number of management personnel, and their management costs, adjustment costs, and transaction costs are relatively high. The research by Chen Jingxue and Bie Shuangzhi
also presents a similar view.
Based on the analysis results of this study, commercial banks in our country can improve their profitability, reduce credit risk, and enhance financial stability by increasing the proportion of personal and corporate loans, thereby achieving sustainable and robust development. It is noteworthy that the financial stability of large-scale banks is paradoxically lower, which should draw the attention of banks and regulatory authorities. They should exercise prudence in securities investment and asset securitization, and in necessary cases, consider staff reduction.
The stable and continuous development of banks is crucial to the normal functioning of the financial market, the stability of the national economy, and the improvement of the national happiness index. The findings of this study are expected to provide useful information for bank management, financial regulation, and economic governance. The issue of lower financial stability in large-scale banks identified in this study requires further in-depth research and investigation and can be the subject of future research.
6. Conclusion
This study provides a comprehensive analysis of how asset allocation strategies among Chinese commercial banks influence their financial stability, with a particular focus on corporate loans, personal loans, and securities investments. The results reveal that an increased allocation to corporate loans is associated with enhanced bank stability, a finding that is supported by the current economic policies and the relatively low risk profile of such loans. Additionally, personal loans, especially housing mortgages, are found to be a significant pillar of financial stability, reflecting the low incidence of non-performing loans in China.
In contrast, the study uncovers a paradox where large-scale banks, despite their size, exhibit lower levels of financial stability. This unexpected outcome is linked to the higher operational and management costs that come with scale, suggesting a need for these institutions to reassess their operational strategies.
The research underscores the broader implications for the financial ecosystem, highlighting the importance of asset management in maintaining the health of financial markets and supporting economic governance. It posits that by adopting a balanced approach to asset allocation, banks can foster a stable and thriving economic environment.
Moving forward, the study suggests that further inquiry into the operational intricacies of large-scale banks is necessary. Delving into their management practices and market responses is crucial for mitigating the stability issues observed.
In summary, the research presents a strategic framework for banks to enhance their financial stability through prudent asset allocation. It advocates for a dynamic and balanced strategy that allows banks to navigate the complexities of an evolving economic landscape and secure long-term stability.
Abbreviations
SME | Medium-Sized Enterprise |
EDF | Expected Default Frequency |
CLP | Corporate Loan Proportion |
PLP | Personal Loan Proportion |
SIP | Securities Investment Proportion |
GAP | Interest Rate Spread |
ASSET | Bank Size |
CPI | Consumer Price Index Growth Rate |
GDP | Gross Domestic Product Growth Rate |
NB | Dummy Variable for Large-Scale Banks |
NBCLP | Cross-Term Large Banks & Corp. Loans |
NBPLP | Cross-Term Large Banks & Pers. Loans |
NBSIP | Cross-Term Large Banks & Sec. Inv |
Author Contributions
Huang Zixin: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Hai Long: Resources, Supervision
Bae Soo Hyun: Validation
Data Availability Statement
The data is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
| [1] |
Naehwang Lee. The Impact of Changes in Domestic Banks' Funding and Operational Structure on Profitability after the Financial Crisis. Ph. D. Thesis, Kyunghee University, 2015.
|
| [2] |
Saunders, A. and M. Cornett. Financial Institutions Management, McGraw Hill. 2003.
|
| [3] |
Acharya, V., I. Hasan, and A. Saunders. Should Banks be Diversified? Evidence from Individual Bank Loan Portfolios. Journal of Business. 2006, 32, 1355-1412.
https://doi.org/10.1086/500679
|
| [4] |
Steve Beck, Tim Ogden. Beware of Bad Microcredit. Harvard Business Review. 2007, 85(9), 20-22.
|
| [5] |
China Banking Regulatory Commission Sichuan Regulatory Bureau Research Group, Wang Jun Quan. Research on the Adjustment Strategy of Bank Credit Structure under the Background of Economic Transformation - A Case Study of Sichuan. Southwest Finance. 2012(07), 7-11.
|
| [6] |
Du Tao. Reflections on the Concentration of Loans in the Tibet Region. Market Research. 2016(02), 41-45.
https://doi.org/10.13999/j.cnki.scyj.2016.02.016
|
| [7] |
Gao Xue Ting. Thoughts on the Adjustment of Commercial Bank Credit Structure. Hebei Finance. 2012, (07), 33-34.
|
| [8] |
Lee, SangWook. Household Loans and Financial Stability. Commercial Education Research. 2016, 30(1), 123-138.
https://doi.org/10.34274/krabe.2016.30.1.006
|
| [9] |
Kim Hyun-jung, Son Jong-chil, Lee Dong-ryul, Lim Hyun-jun, and Na Seung-ho. Analysis of the Causes of Household Debt Increase and Sustainability in Our Country. Bank of Korea Economic Review. 2013(8), 1-52.
|
| [10] |
Huang Zi Xin and Bae Soo Hyun. A Study on the Effect of Household Loans on Financial Soundness in Banks. The Journal of the Convergence on Culture Technology (JCCT). 2021, 7(4), 1-7.
https://doi.org/10.17703/JCCT.2021.7.4.1
|
| [11] |
Kang Taek-ho. The Current Status of Banknote Issuance: A Case Study. Finance. 1995(7).
|
| [12] |
Xu Heng. Design of Credit Management Plan for Micro and Small Enterprises Loan. Master's Thesis, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2009.
|
| [13] |
Yuan Gang, Liu Hui Feng. A Brief Discussion on the Credit Risk Management of Banks to SMEs in China. Shanghai Finance. 2010(07), 89-91.
|
| [14] |
Xu Shuying. Research on the Impact of Bond Investment on Commercial Bank Risk Taking. Review of Financial & Technological Economics. 2023(03), 68-87.
|
| [15] |
Bai Yun. A Preliminary Discussion on the Innovation of Commercial Bank Financial Investment Business. Times Finance. 2016(33), 91-92.
|
| [16] |
Xu Yan. Analysis of the Risk of Commercial Bank Bond Investment under the New Normal. Business News. 2020(05), 82.
|
| [17] |
Han Sang-seop and Lee Byung-yun. The Effects of Korean Banks' Funding Structure on Their Profitability and Management Stability. Korea Institute of Finance (KIF) Research Report. 2012(5), 1-89.
|
| [18] |
Jong Ku Kang. Analysis of Factors Affecting Banks` Wholesale Funding Ratio. Kukje Kyungje Yongu. 2010, 16(3), 21-49.
https://doi.org/10.17298/KKY.2010.16.3.002
|
| [19] |
John H. Boyd, David E. Runkle. Size and performance of banking firms: Testing the predictions of theory, Journal of Monetary Economics. 1993, 31(1), 47-67.
https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3932(93)90016-9
|
| [20] |
Chen Jingxue and Bie Shuangzhi. An Empirical Analysis of and Sug gestions on the Efficiency of Scale Economy of Our State-Owned Commercial Banks. Finance Forum. 2004(10), 46-50+63.
https://doi.org/10.16529/j.cnki.11-4613/f.2004.10.008
|
| [21] |
Wahyu Yuwana Hidayat, Makoto Kakinaka, Hiroaki Miyamoto. Bank risk and non-interest income activities in the Indonesian banking industry. Journal of Asian Economics. 2012. 23(4), 335-343.
|
| [22] |
All-China Federation of Industry and Commerce Real Estate Chamber, Chen Hongbo, Wang Zhen. A Study on the Macro-Financial Risks of China's Real Estate. Finance & Trade Economics. 2006(05): 11-16+96.
https://doi.org/10.19795/j.cnki.cn11-1166/f.2006.05.002
|
Cite This Article
-
-
@article{10.11648/j.mcs.20240904.11,
author = {Huang Zixin and Hai Long and Bae Soo Hyun},
title = {Asset Allocation and Bank Resilience: China Insights
},
journal = {Mathematics and Computer Science},
volume = {9},
number = {4},
pages = {64-73},
doi = {10.11648/j.mcs.20240904.11},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mcs.20240904.11},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.mcs.20240904.11},
abstract = {This research is based on the panel data from the annual reports of Chinese commercial banks for the years 2010-2020. A panel data model is constructed to empirically investigate the influence of commercial banks' asset allocation on financial stability. The study innovatively explores the differences between large-scale banks and general-scale banks in this context, as well as the interaction effects between large-scale banks and their methods of capital application. The findings indicate that: firstly, the higher the proportion of corporate loans in commercial banks, the stronger the stability. With the support of national policies, the operating environment for emerging industries has improved, leading to a reduction in bankruptcy risks and further decreasing the credit risk of related banks, which contributes to the enhancement of banks' financial stability. Additionally, compared to securities investments affected by market fluctuations, corporate loans are less susceptible to significant capital changes, and their risks are primarily determined by the operating conditions of the related enterprises, making them relatively controllable. Secondly, the higher the proportion of personal loans in commercial banks, the stronger the stability. The largest part of personal loans consists of housing mortgage loans, which have a low non-performing loan rate and high quality in China. Therefore, an increase in personal loans helps to enhance the financial stability of banks. Thirdly, large-scale banks exhibit lower financial stability. Due to the redundancy in management personnel in large-scale banks, management costs, adjustment costs, and transaction costs are relatively high. Furthermore, it is worth noting that because large-scale banks hold a significant amount of surplus funds, they are prone to excessive securities investments. Fluctuations in the securities market increase external risks and decrease financial stability.
},
year = {2024}
}
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
-
TY - JOUR
T1 - Asset Allocation and Bank Resilience: China Insights
AU - Huang Zixin
AU - Hai Long
AU - Bae Soo Hyun
Y1 - 2024/09/06
PY - 2024
N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mcs.20240904.11
DO - 10.11648/j.mcs.20240904.11
T2 - Mathematics and Computer Science
JF - Mathematics and Computer Science
JO - Mathematics and Computer Science
SP - 64
EP - 73
PB - Science Publishing Group
SN - 2575-6028
UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.mcs.20240904.11
AB - This research is based on the panel data from the annual reports of Chinese commercial banks for the years 2010-2020. A panel data model is constructed to empirically investigate the influence of commercial banks' asset allocation on financial stability. The study innovatively explores the differences between large-scale banks and general-scale banks in this context, as well as the interaction effects between large-scale banks and their methods of capital application. The findings indicate that: firstly, the higher the proportion of corporate loans in commercial banks, the stronger the stability. With the support of national policies, the operating environment for emerging industries has improved, leading to a reduction in bankruptcy risks and further decreasing the credit risk of related banks, which contributes to the enhancement of banks' financial stability. Additionally, compared to securities investments affected by market fluctuations, corporate loans are less susceptible to significant capital changes, and their risks are primarily determined by the operating conditions of the related enterprises, making them relatively controllable. Secondly, the higher the proportion of personal loans in commercial banks, the stronger the stability. The largest part of personal loans consists of housing mortgage loans, which have a low non-performing loan rate and high quality in China. Therefore, an increase in personal loans helps to enhance the financial stability of banks. Thirdly, large-scale banks exhibit lower financial stability. Due to the redundancy in management personnel in large-scale banks, management costs, adjustment costs, and transaction costs are relatively high. Furthermore, it is worth noting that because large-scale banks hold a significant amount of surplus funds, they are prone to excessive securities investments. Fluctuations in the securities market increase external risks and decrease financial stability.
VL - 9
IS - 4
ER -
 Copy
|
Copy
|
 Download
Download
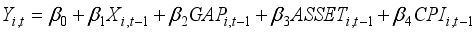
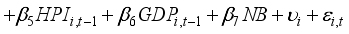 (1)
(1) 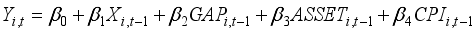
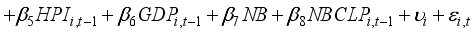 (2)
(2) 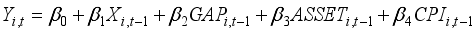
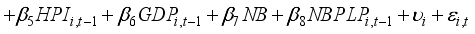 (3)
(3) 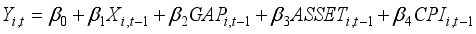
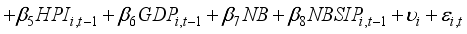 (4)
(4)