Object: Real-world study was chose to compare efficacies of rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapies in eradicating primary Helicobacter pylori infection, and accumulate evidence for choosing appropriate Helicobacter pylori eradicative therapy. Methods: Non-interventive, multi-center studies was conducted to collect patients who took proton pump inhibitor bismuth quadruple therapy from January 2019 to December 2023. Duration was 14 days. Patients were divided into rabeprazole or esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy. Helicobacter pylori were determined using 13C/14C urea breath test at least 4 weeks after completion of treatments. Results: Four hundred and sixty-seven patients were enrolled: 110 and 367 patients in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively. Baseline variables were balanced between the two groups using a propensity score matching. 110 and 274 patients in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively. Eradicative incidences were 82.7% (91/110) and 86.1% (236/276) in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively, and and there was no significant difference (P > 0.05). Conclusions: Rabeprazole or esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy could be chose similarly for eradicating primary Helicobacter pylori infection.
| Published in | Science Discovery (Volume 13, Issue 3) |
| DOI | 10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14 |
| Page(s) | 56-59 |
| Creative Commons |
This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, provided the original work is properly cited. |
| Copyright |
Copyright © The Author(s), 2025. Published by Science Publishing Group |
Rabeprazole, Esomeprazole, Bismuth, Helicobacter pylori, Real-world Study
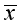 ±SD表示,否则以M(Q25, Q75)表示;两组数据如符合方差齐性与正态性,则采用参数检验t检验,否则选用非参数检验Mann-Whitney 检验;分类资料采用χ2检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
±SD表示,否则以M(Q25, Q75)表示;两组数据如符合方差齐性与正态性,则采用参数检验t检验,否则选用非参数检验Mann-Whitney 检验;分类资料采用χ2检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。 基线指标 | 匹配前 | 匹配后 | ||||||
雷贝拉唑铋剂四联组(110例) | 艾司奥美拉唑铋剂四联组(367例) | 统计值 | P值 | 雷贝拉唑铋剂四联组(110例) | 艾司奥美拉唑铋剂四联组(274例) | 统计值 | P值 | |
性别(男/女,例) | 35/75 | 150/217 | χ2=2.9 | P=0.08 | 35/75 | 110/164 | χ2=2.3 | P=0.13 |
年龄(M(Q25, Q75),岁) | 52(44, 58) | 55(47, 64) | U=16756 | P=0.007 | 52(44, 58) | 54(46, 60) | U=13259 | P=0.07 |
组别 | 根除例数 | 未根除例数 | 统计值 | P值 |
雷贝拉唑铋剂四联组 | 91 | 19 | χ2=0.72 | P=0.40 |
艾司奥美拉唑铋剂四联组 | 236 | 38 |

蒲强红(1981-12),男,汉族,四川眉山,副主任药师,博士,研究方向:临床药学,办公室电话:0833-2119476,E-mail:243937683@qq.com |
| [1] | Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, Rokkas T, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report [J]. Gut, 2022, 71:1724-1762. |
| [2] | 中华医学会消化病学分会幽门螺杆菌学组. 2022中国幽门螺杆菌感染治疗指南 [J]. 胃肠病学, 2022, 27(3): 150-162. |
| [3] | Asim M, Baqai K, Abbas Z, et al. Addition of bismuth to standard triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a randomised controlled trial [J]. J Pak Med Assoc, 2020, 70(8): 1334-1339. |
| [4] | Kadayifci A, Uygun A, Polat Z, et al. Comparison of bismuth-containing quadruple and concomitant therapies as a first-line treatment option for Helicobacter pylori[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2012, 23(1):8-13. |
| [5] | Hsu P I, Tsay F W, Graham D Y, et al. Equivalent Efficacies of Reverse Hybrid and Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection in a Randomized Controlled Trial [J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16(9): 1427-1433. |
| [6] | Koroglu M, Ayvaz M A, Ozturk M A. The efficacy of bismuth quadruple therapy, sequential therapy, and hybrid therapy as a first-line regimen for Helicobacter pylori infection compared with standard triple therapy [J]. Niger J Clin Pract, 2022, 25(9): 1535-1541. |
| [7] | Mcnicholl A G, Linares P M, Nyssen O P, et al. Meta-analysis: esomeprazole or rabeprazole vs. first-generation pump inhibitors in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection [J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2012, 36(5): 414-425. |
| [8] | 刘伟峰,田继红,刘景霞. 雷贝拉唑钠四联方案治疗幽门螺杆菌阳性十二指肠溃疡的疗效观察 [J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析, 2017, 17(6): 785-786, 789. |
| [9] | 刘佐相,龙子临,杨智荣,等. 临床干预措施效力-效果差距弥合的方法学研究进展(二):增强临床试验结果的外推性[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2024, 45(4): 579-584. |
| [10] | 廖珊妹,张小娟,张晓薇,等. 真实世界研究的方法学进展 [J]. 中国食品药品监管, 2021(4): 32-43. |
| [11] | 张鑫赫,曾子露,王雪,等. 雷贝拉唑与艾司奥美拉唑钠治疗幽门螺杆菌感染疗效及安全性比较 [J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41(10): 885-889. |
| [12] | Graham D Y, Lu H, Yamaoka Y. A report card to grade Helicobacter pylori therapy [J]. Helicobacter, 2007, 12(4): 275-278. |
| [13] | Kyoungwon Jung, Sam Ryong Jee, Moon Won Lee, et al. Comparison of Helicobacter pylori eradication rates between 7 and 14 days of tailored therapy according to clarithromycin resistance test: A randomized, multicenter, non-inferiority study [J]. Helicobacter. 2024, 29(3): e13084. |
| [14] | Faming Yang, Baiyang Yu, Lang Qin, et al. A randomized clinical study on the efficacy of vonoprazan combined with amoxicillin duo regimen for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori [J]. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13; 102(41): e35610. |
| [15] | Baojun Suo, Xueli Tian, Hua Zhang, et al. Bismuth, esomeprazole, metronidazole, and minocycline or tetracycline as a first-line regimen for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized controlled trial [J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2023, 136(8): 933-940. |
| [16] | Kuo-Tung Hung, Shih-Cheng Yang, Cheng-Kun Wu, et al. Eradication Rates for Esomeprazole and Lansoprazole-Based 7-Day Non-Bismuth Concomitant Quadruple Therapy for First-Line Anti- Helicobacter pylori Treatment in Real World Clinical Practice [J]. Infect Drug Resist 2021, 14: 1239-1246. |
| [17] | Wang Y, Dai X, Gao C, et al. Network meta-analysis of different dosages of esomeprazole and rabeprazole for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori [J]. Helicobacter, 2023, 28(2): e12948. |
APA Style
Pu, Q., Deng, Y., Zhou, J., Luo, M. (2025). Multi-center Comparison of Rabeprazole and Esomeprazole Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Treatment of Primary Helicobacter pylori Infection. Science Discovery, 13(3), 56-59. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14
ACS Style
Pu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Luo, M. Multi-center Comparison of Rabeprazole and Esomeprazole Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Treatment of Primary Helicobacter pylori Infection. Sci. Discov. 2025, 13(3), 56-59. doi: 10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14
@article{10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14,
author = {Qiang-Hong Pu and Yuan-Qian Deng and Jian Zhou and Ming-Xing Luo},
title = {Multi-center Comparison of Rabeprazole and Esomeprazole Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Treatment of Primary Helicobacter pylori Infection},
journal = {Science Discovery},
volume = {13},
number = {3},
pages = {56-59},
doi = {10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14},
url = {https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14},
eprint = {https://article.sciencepublishinggroup.com/pdf/10.11648.j.sd.20251303.14},
abstract = {Object: Real-world study was chose to compare efficacies of rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapies in eradicating primary Helicobacter pylori infection, and accumulate evidence for choosing appropriate Helicobacter pylori eradicative therapy. Methods: Non-interventive, multi-center studies was conducted to collect patients who took proton pump inhibitor bismuth quadruple therapy from January 2019 to December 2023. Duration was 14 days. Patients were divided into rabeprazole or esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy. Helicobacter pylori were determined using 13C/14C urea breath test at least 4 weeks after completion of treatments. Results: Four hundred and sixty-seven patients were enrolled: 110 and 367 patients in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively. Baseline variables were balanced between the two groups using a propensity score matching. 110 and 274 patients in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively. Eradicative incidences were 82.7% (91/110) and 86.1% (236/276) in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively, and and there was no significant difference (P > 0.05). Conclusions: Rabeprazole or esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy could be chose similarly for eradicating primary Helicobacter pylori infection.},
year = {2025}
}
TY - JOUR T1 - Multi-center Comparison of Rabeprazole and Esomeprazole Bismuth Quadruple Therapies in Treatment of Primary Helicobacter pylori Infection AU - Qiang-Hong Pu AU - Yuan-Qian Deng AU - Jian Zhou AU - Ming-Xing Luo Y1 - 2025/06/25 PY - 2025 N1 - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14 DO - 10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14 T2 - Science Discovery JF - Science Discovery JO - Science Discovery SP - 56 EP - 59 PB - Science Publishing Group SN - 2331-0650 UR - https://doi.org/10.11648/j.sd.20251303.14 AB - Object: Real-world study was chose to compare efficacies of rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapies in eradicating primary Helicobacter pylori infection, and accumulate evidence for choosing appropriate Helicobacter pylori eradicative therapy. Methods: Non-interventive, multi-center studies was conducted to collect patients who took proton pump inhibitor bismuth quadruple therapy from January 2019 to December 2023. Duration was 14 days. Patients were divided into rabeprazole or esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy. Helicobacter pylori were determined using 13C/14C urea breath test at least 4 weeks after completion of treatments. Results: Four hundred and sixty-seven patients were enrolled: 110 and 367 patients in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively. Baseline variables were balanced between the two groups using a propensity score matching. 110 and 274 patients in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively. Eradicative incidences were 82.7% (91/110) and 86.1% (236/276) in rabeprazole and esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy respectively, and and there was no significant difference (P > 0.05). Conclusions: Rabeprazole or esomeprazole bismuth quadruple therapy could be chose similarly for eradicating primary Helicobacter pylori infection. VL - 13 IS - 3 ER -