-

Kinetic Model for Anaerobic Digestion of Distillery Spent Wash
Pooja Sharma,
Uttam Kumar Ghosh,
Amiya Kumar Ray
Issue:
Volume 4, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
139-146
Received:
21 July 2016
Accepted:
2 August 2016
Published:
15 November 2016
Abstract: Kinetic studies were carried out for anaerobic digestion of distillery spent wash considering growth kinetic models due to Monod and Contois. The kinetic parameters were predicted with the help of previously published experimental data for anaerobically treated distillery spent wash. The digester was operated at seven different values of loading rates ranging between 0.954 to 2.459 gCOD/L/day. Maximum specific growth rate and maximum specific substrate utilization rate for Monod model have been predicted as of the order of 0.153 g/g/day 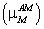 and 3.06 g/g/day
and 3.06 g/g/day 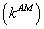 , respectively, and those for Contois kinetic model were found to be 0.140 g/g/day
, respectively, and those for Contois kinetic model were found to be 0.140 g/g/day 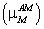 and 0.421 g/g/day
and 0.421 g/g/day 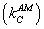 , respectively. However, for both the models the decay rate coefficient,
, respectively. However, for both the models the decay rate coefficient, 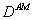 was calculated as 0.0131 g/g/day. The estimated value of empirical constant
was calculated as 0.0131 g/g/day. The estimated value of empirical constant 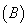 in Contois model was found to be order of 0.699 (dimensionless). The deviation of model predicted values from experimental results has been compared. Sensitivity analysis of the developed models was carried out by considering 10% increase in the values of both
in Contois model was found to be order of 0.699 (dimensionless). The deviation of model predicted values from experimental results has been compared. Sensitivity analysis of the developed models was carried out by considering 10% increase in the values of both 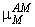 and
and 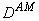 .
Abstract: Kinetic studies were carried out for anaerobic digestion of distillery spent wash considering growth kinetic models due to Monod and Contois. The kinetic parameters were predicted with the help of previously published experimental data for anaerobically treated distillery spent wash. The digester was operated at seven different values of loading ra...
Show More
.
Abstract: Kinetic studies were carried out for anaerobic digestion of distillery spent wash considering growth kinetic models due to Monod and Contois. The kinetic parameters were predicted with the help of previously published experimental data for anaerobically treated distillery spent wash. The digester was operated at seven different values of loading ra...
Show More
-

Analysis of Adsorption Technologies of Water and Wastewater Treatment Used in the Republic of Moldova
Tudor Lupascu,
Igor Povar
Issue:
Volume 4, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
147-153
Received:
10 October 2016
Accepted:
8 November 2016
Published:
29 November 2016
Abstract: In this paper, it has been proved that in wastewater purification technology from dyes the adsorption methods ensure practically the complete removal of all dyes. Modified activated carbons, obtained by semi-industrial scale from local renewable raw materials such as cobs, nut shells and grape seeds, have been tested for use in the detoxification technologies of aquatic environment. A significant role in this research is given to adsorption mechanisms of refractory substances on carbon adsorbents. As a result of the physicochemical study of adsorption processes, a scheme of the wastewater purification from dyes has been developed. Their amplified efficiency, in comparison to imported activated carbons, has been demonstrated in experiments, carried out at stations of surface water and groundwater purification, as well as at wastewater treatment plants. At this time, scientific research of the feasibility study and business plan for the economic unit of production of activated carbons, based on local raw materials in the Republic of Moldova, is in progress.
Abstract: In this paper, it has been proved that in wastewater purification technology from dyes the adsorption methods ensure practically the complete removal of all dyes. Modified activated carbons, obtained by semi-industrial scale from local renewable raw materials such as cobs, nut shells and grape seeds, have been tested for use in the detoxification t...
Show More
-

Transesterification and Production of Biodiesel from Waste Cooking Oil: Effect of Operation Variables on Fuel Properties
Issue:
Volume 4, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
154-160
Received:
17 November 2016
Accepted:
1 December 2016
Published:
5 January 2017
Abstract: Biodiesel is proved to be the best replacement for diesel because of its unique properties like low toxicity, no sulfur emissions, no particulate matter pollutants, significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and biodegradability. Several processes for biodiesel fuel production have been developed, among which transesterification using alkali catalysis gives high levels of conversion of triglycerides to their corresponding methyl esters in short reaction times. It is prepared from waste vegetable oils and animal fats by trans-esterification process. It is alkali catalyzed reaction which involves waste cooking oil, methanol, and potassium hydroxide. The study focus on the physical and chemical properties of waste cooking oil (WCO), transesterification and production of biodiesel from WCO. The operation variables used were methanol/oil molar ratio (5:1-9:1), catalyst concentration (0.5-2.0 wt%), temperature (30-70°C). The evolution of the process was followed by gas chromatography, determining the concentration of the methyl esters at different reaction times. The biodiesel was characterized by its density, viscosity, high heating value, cetane index, cloud and pour points, characteristics of distillation, flash and combustion points, saponification value, and iodine value according to ISO norms. The biodiesel with the best properties was obtained using a methanol/oil molar ratio of 6:1, potassium hydroxide as catalyst (1%), and 60°C temperature. This biodiesel had properties very similar to those of no. 2 diesel.
Abstract: Biodiesel is proved to be the best replacement for diesel because of its unique properties like low toxicity, no sulfur emissions, no particulate matter pollutants, significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and biodegradability. Several processes for biodiesel fuel production have been developed, among which transesterification using alkali...
Show More
-

A Fresh Look at the Kinetics of Pentosan Removal from Lignocellulosic Biomass
Surendra Pratap Yadav,
Uttam Kumar Ghosh,
Amiya Kumar Ray
Issue:
Volume 4, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
161-169
Received:
4 October 2016
Accepted:
13 October 2016
Published:
7 January 2017
Abstract: The effect of time, temperature and concentration of prehydrolyzing agent on the biomass prehydrolysis have been studied for pentosan removal. Basic kinetic parameters i.e. rate constant, order of reaction, energy of activation and frequency factor were calculated. This study on the kinetics of pentosan removal reveals that the rate of pentosan removal does not follow exactly first order kinetics and shifting of order is observed during the reaction. In searching for a kinetic equation for pentosan removal, it was found that the data was well fitted by an order at higher concentration and by another order at lower concentration of prehydrolyzing agent. The order of reaction of pentosan removal lies between 0.8 to 1.40. A regression model was developed for % pentosan removal relating to temperature and time for water prehydrolysis at higher temperatures. This model was well fitted by data given in literature.
Abstract: The effect of time, temperature and concentration of prehydrolyzing agent on the biomass prehydrolysis have been studied for pentosan removal. Basic kinetic parameters i.e. rate constant, order of reaction, energy of activation and frequency factor were calculated. This study on the kinetics of pentosan removal reveals that the rate of pentosan rem...
Show More
-

Use of Hydrous Manganese Oxides Nanopowders as a Potential Sorbent for Selective Removal of Nickel Ions from Industrial Waste Water, Kinetics and Isotherm Studies
R. Ghaniem,
Y. A. El-Taweil,
M. E. Ossman
Issue:
Volume 4, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
170-178
Received:
19 November 2016
Accepted:
1 December 2016
Published:
12 January 2017
Abstract: Hydrous Manganese Oxides Nanopowders as nano adsorbent (MONs) was synthesized and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The adsorption of Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution on the MONs was investigated with variations in contact time, pH, initial Ni (II) concentration and adsorbent dosage. The results showed that the adsorption of Ni (II) onto MONs increased within 25 min and reached equilibrium gradually and removal percentage were 83%, 57%, 42% and 35% for 25 ppm, 50 ppm, 75 ppm and 100 ppm Ni (II), respectively, by using 1g/l MONs for 90 min at pH 6. The adsorption behavior of Ni (II) onto MONs was best described by the pseudo-second-order model and Freundlish isotherm. The results also indicated that the type of adsorption involved in this study is physiosorption (physical sorption) which usually takes place at low temperature. The results also revealed that MONs was a promising adsorbent for removal of Ni ions from industrial wastewater.
Abstract: Hydrous Manganese Oxides Nanopowders as nano adsorbent (MONs) was synthesized and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The adsorption of Ni (II) ions from aqueous solution on the MONs was investigated with variations in contact time, pH, initial Ni (II) concentrat...
Show More
-

Chemical Composition, Sensory Evaluation and Starter Activity in Cow, Soy, Peanut and Rice Milk
Mohamed Ismail Abou-Dobara,
Magdy Mohamed Ismail,
Nawal Mohamed Refat
Issue:
Volume 4, Issue 6, November 2016
Pages:
179-186
Received:
29 August 2016
Accepted:
3 January 2017
Published:
13 January 2017
Abstract: The aim of this work was to study the effect of mixing various levels of soy, peanut or rice milk with cow milk on the chemical composition, sensory attributes, starter activity and culture bacteria counts during fermentation. The results showed that no clear differences in titratable acidity, pH and redox potential (Eh) values were noticed between cow or soy milk while acidity and Eh levels of peanut and rice milk were lower than those of cow milk. Total solids, fat, total protein and ash concentrations of cow milk were slightly higher than those of soy and rice milk. Peanut milk was richer in fat but poorer in ash than cow milk. Color, appearance, smell, taste, mouth feel, texture and body scores of cow milk were higher than those of soy, peanut or rice milk but rice milk gained the highest scores of color and appearance. Incorporation of cow milk with soy or peanut milk improved its sensory evaluation scores. Both acidity ratios and the development of acidity rates within fermentation were higher in cow milk than that of soy, peanut or rice milk. Culture bacteria not only were able to grow in soy, peanut or rice milk but also their numbers and viability were higher in them as compared with cow milk. Furthermore, incorporation of soy, peanut and rice milk with cow milk increased this influence.
Abstract: The aim of this work was to study the effect of mixing various levels of soy, peanut or rice milk with cow milk on the chemical composition, sensory attributes, starter activity and culture bacteria counts during fermentation. The results showed that no clear differences in titratable acidity, pH and redox potential (Eh) values were noticed between...
Show More





